(2) 機器學習最強入門:基礎數學/機率/統計邁向AI真實數據
邏輯迴歸 - 信用卡,葡萄酒,糖尿病
邏輯迴歸觀念
邏輯迴歸(logistic Regression)是一種常見的統計分析模型,邏輯迴歸經過一個邏輯(或稱 sigmoid)函數轉換,將輸出限制在0~1之間
應用邏輯函數
線性函數觀念 :
$y = \beta_0 + \beta_1x$
將上述函數玷辱 Sigmoid 函數得到以下結果 :
$ f(x) = \frac{1}{e^{-x}} = \frac{1}{e^{-(\beta_0 + \beta_1x)}} $
有時以下列公式表示邏輯迴歸模型 :
$ P(Y=1|X) = \frac{1}{e^{-(\beta_0 + \beta_1x)}} $
P(Y=1|X) 代表給定變數X下,Y等於1的機率,實務上是使用大概似估計法(Maximum Linkelihood Estimation,MLE)來進行求解
1 | # 邏輯迴歸運算 |
邏輯迴歸模型基礎應用
邏輯迴歸模型語法基礎
1 | from joblib import dump |
1 | # 測試應用公式 |
多分類演算法



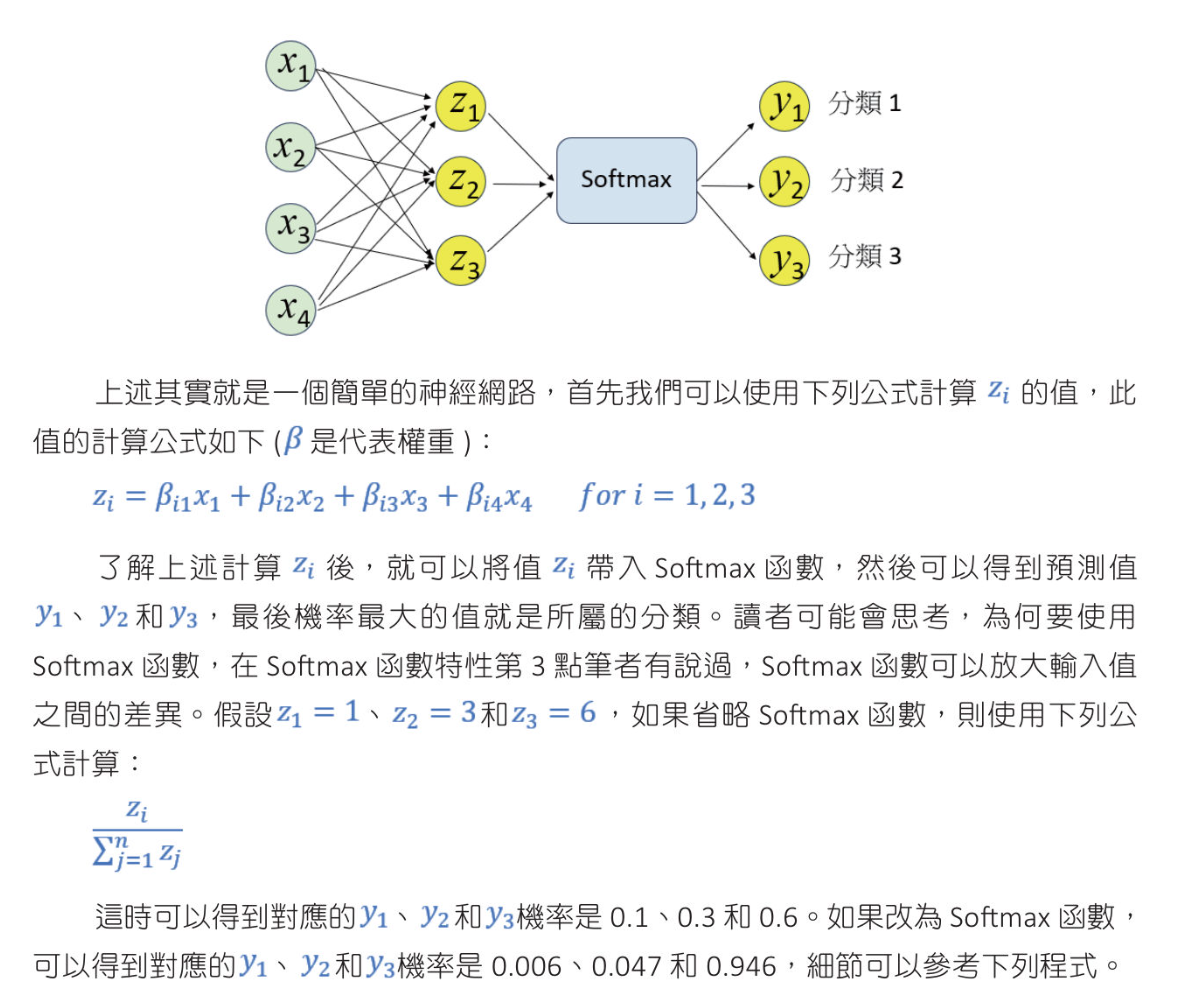
1 | from math import exp |
信用卡數據集計算
數據集內容

挑選重要特徵
1 | # 繪出特徵值 |
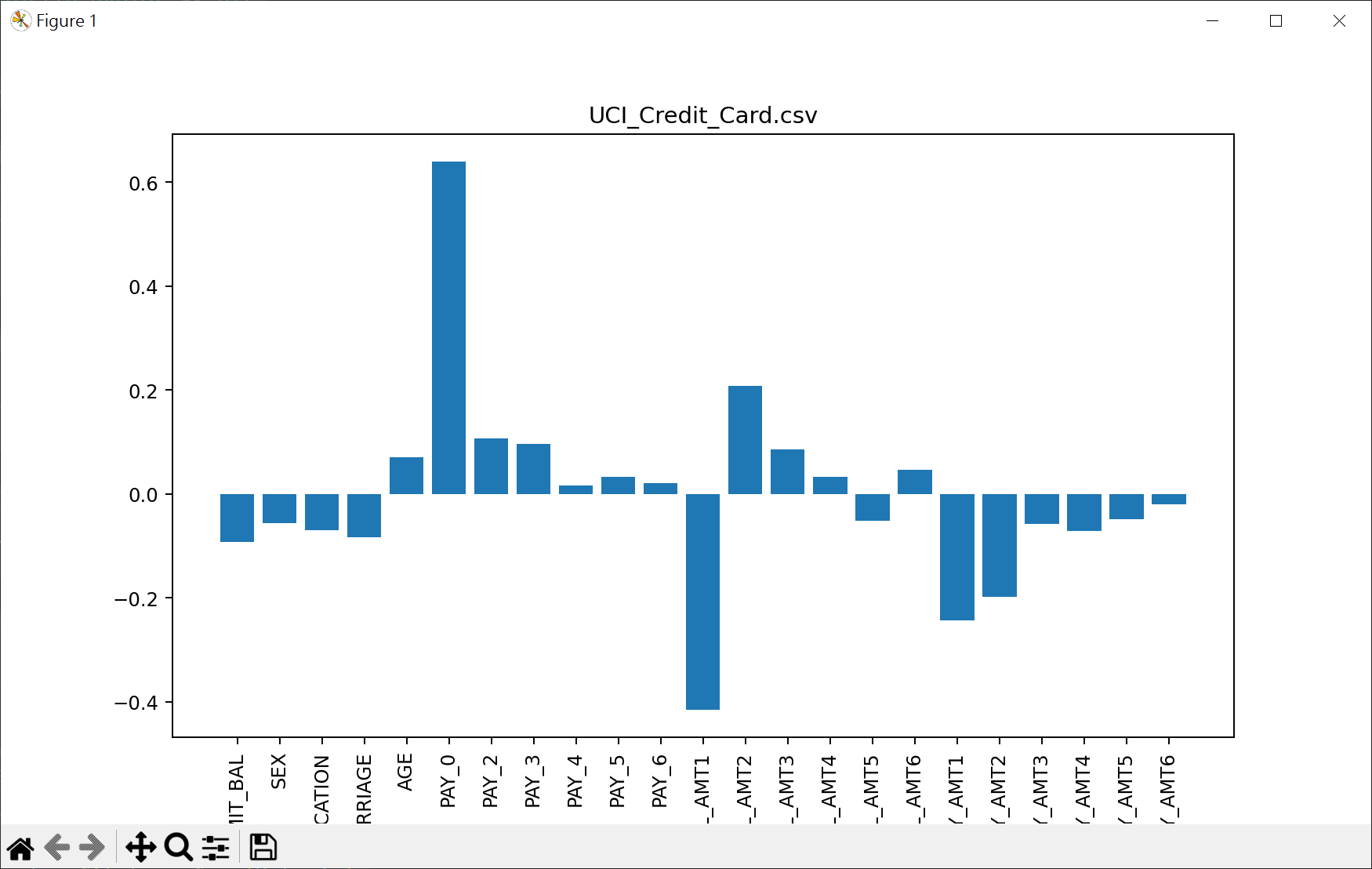
用最相關2個特徵,設計邏輯迴歸模型
1 | # 用最相關2個特徵,設計邏輯迴歸模型 |
用最全部特徵,設計邏輯迴歸模型(差異不大)
1 | # 用最全部特徵,設計邏輯迴歸模型 |
葡萄酒數據
數據內容

1 | from sklearn import datasets |
使用邏輯演算法執行葡萄酒分類
1 | from sklearn.datasets import load_wine |
糖尿病數據
數據內容

1 | import pandas as pd |
處理潛在缺失值(0)

1 | # 中位數填補區失值 |
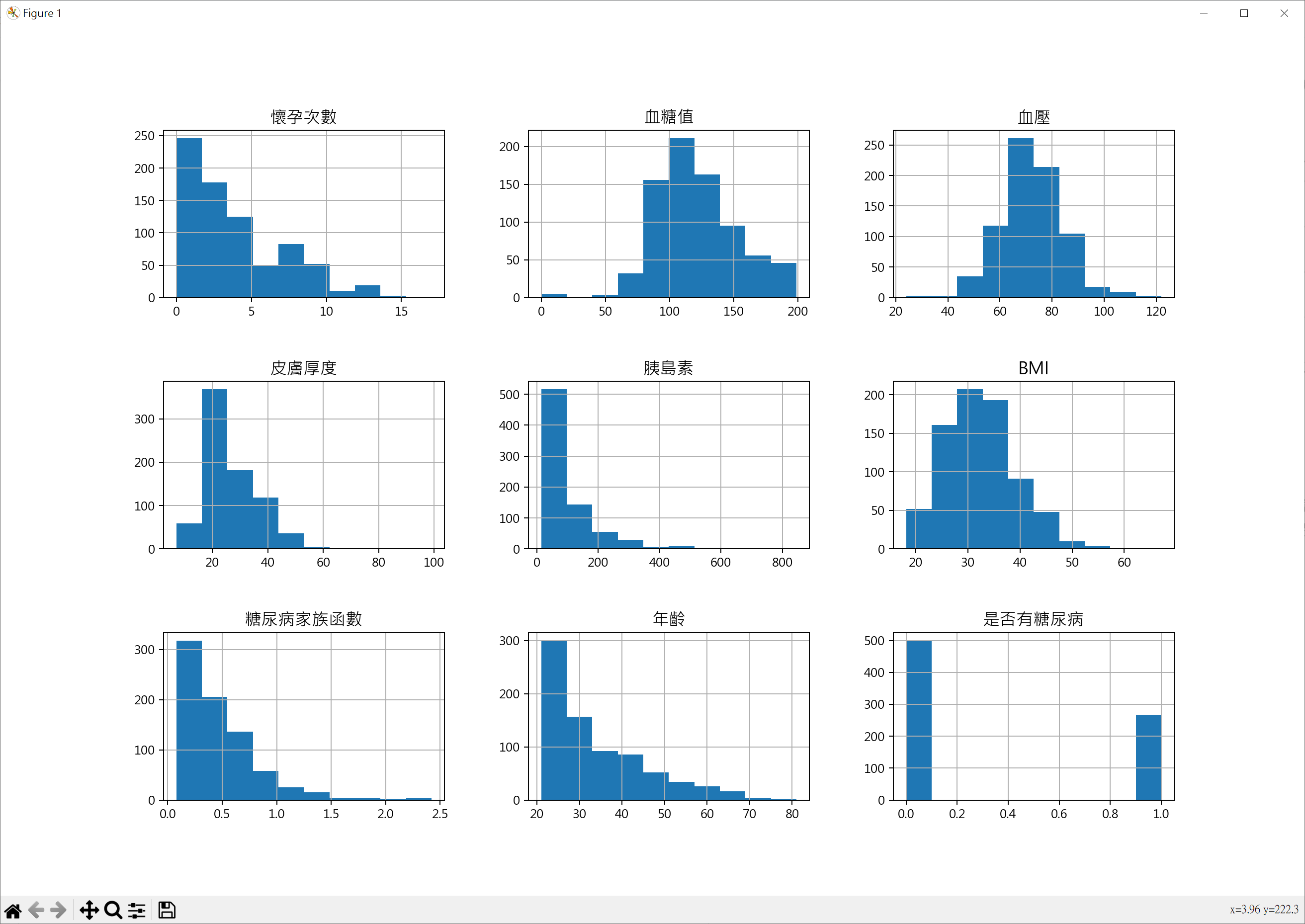
特徵直方圖
1 | import pandas as pd |
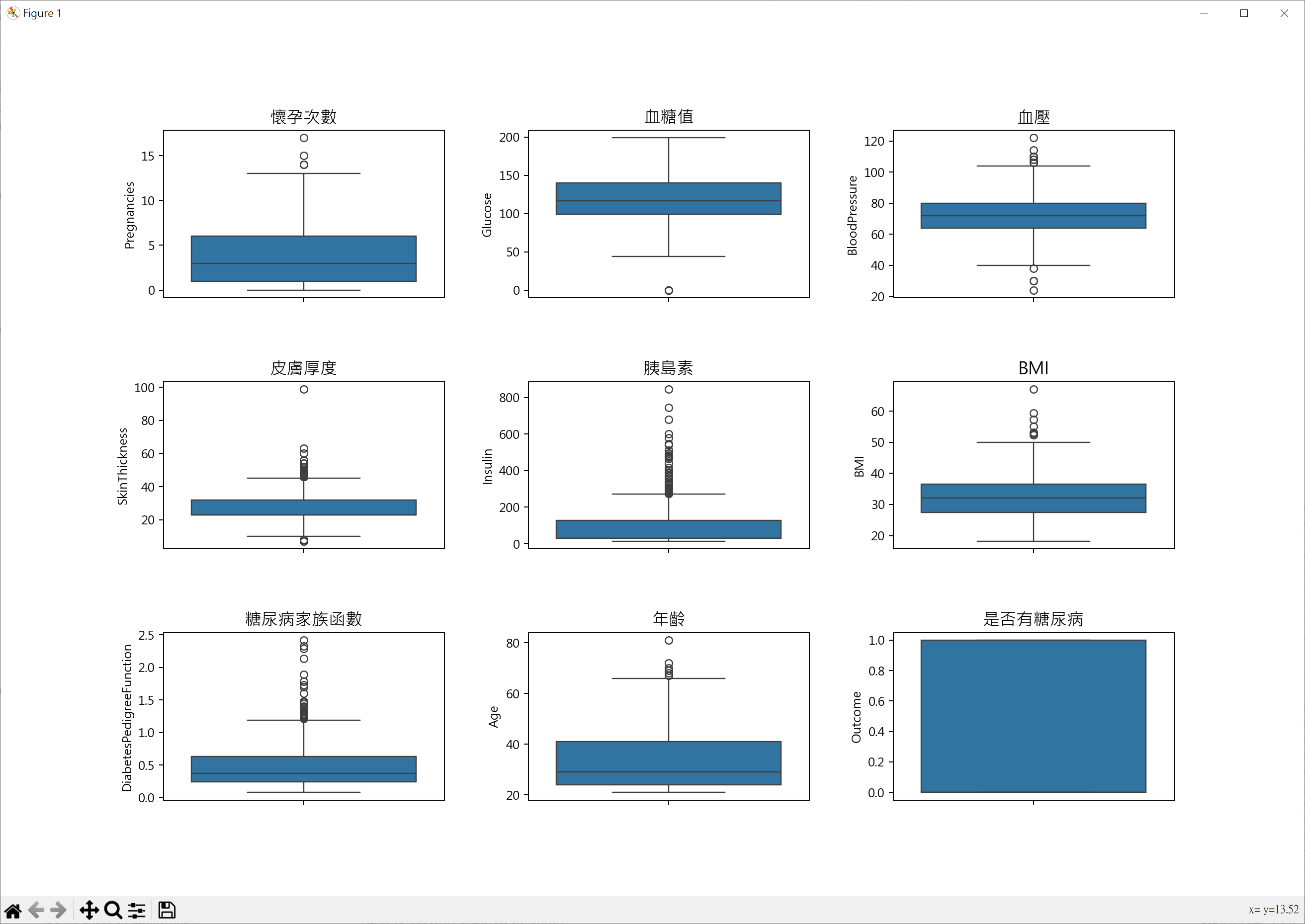
特徵箱形圖
1 | import pandas as pd |
用所有特徵做糖尿病患者預估
1 | import pandas as pd |
繪製皮爾遜相關係數熱圖
1 | import pandas as pd |
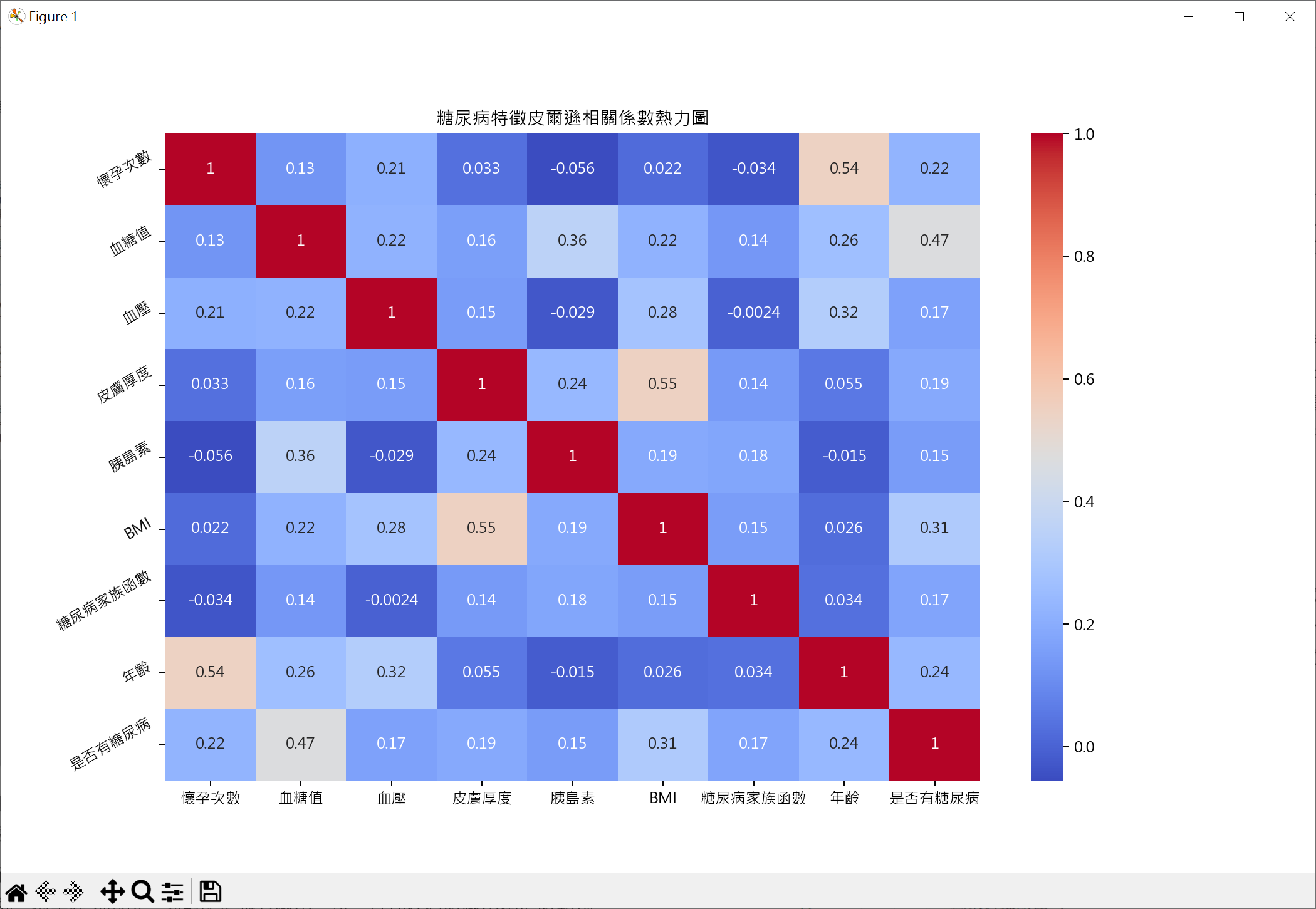
用最相關皮爾遜相關係數做糖尿病預估
1 | import pandas as pd |
決策樹 - 葡萄酒,鐵達尼號,Telco,Retail
決策樹觀念

應用在分類問題

應用在迴歸問題


天氣數據應用
建立決策樹模型


天氣數據實例
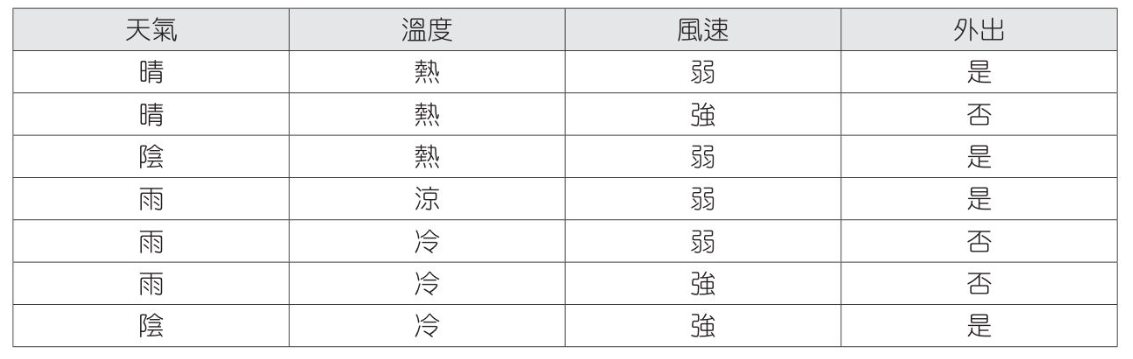
1 | from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder |
葡萄酒數據 - 分類應用
預設條件處理葡萄酒數據
1 | from sklearn.datasets import load_wine |
使用兩個特徵,更改深度
1 | from sklearn.datasets import load_wine |
繪製決策樹
安裝
- 安裝 Graphviz
1
pip install graphviz
- 下載 graphviz program
- 解壓縮至 computer
- set path
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20# set from vscode example
{
"terminal.integrated.profiles.windows": {
"PowerShell": {
"source": "PowerShell",
"env": {
"PATH": "${env:PATH};D:\\app\\python_other\\Graphviz-12.0.0-win64\\bin"
}
},
"Command Prompt": {
"path": [
"${env:windir}\\System32\\cmd.exe"
],
"env": {
"PATH": "${env:PATH};D:\\app\\python_other\\Graphviz-12.0.0-win64\bin"
}
}
},
"terminal.integrated.defaultProfile.windows": "PowerShell"
}
繪製
1 | # 繪製決策樹 |
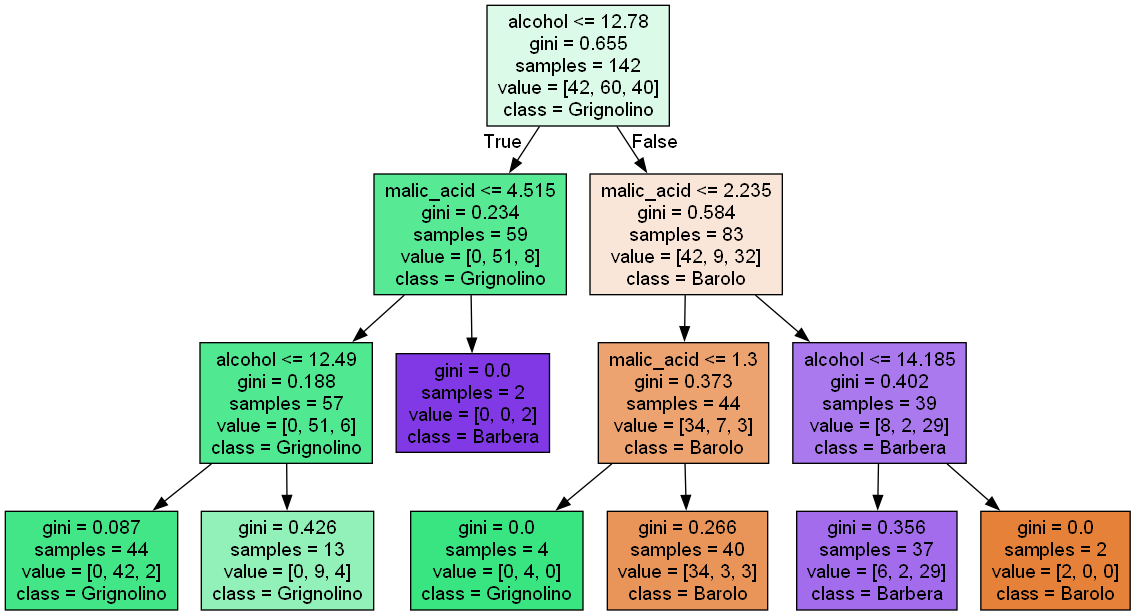
- 使用 gini 演算法
- value 表示各類別包含數量
- 顏色表示歸類類別
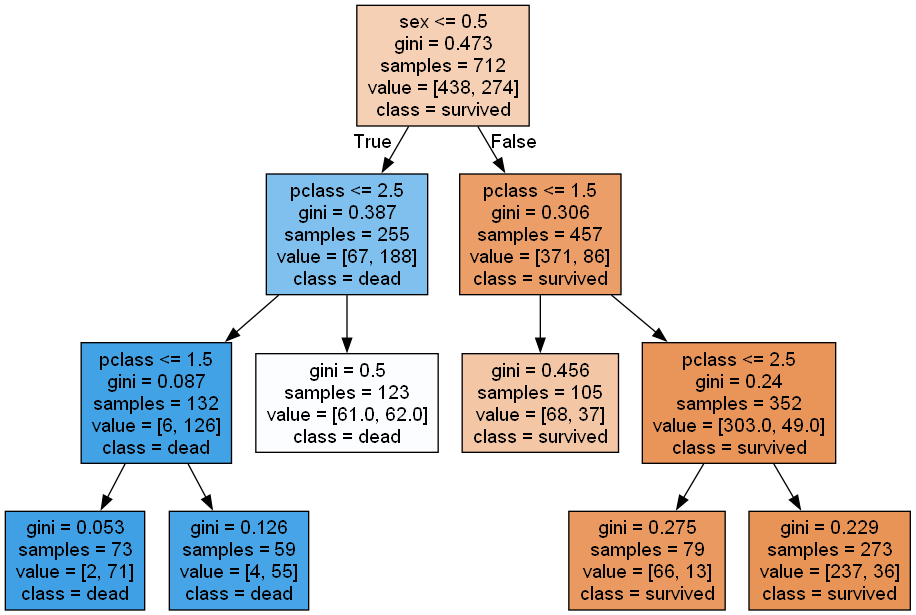
鐵達尼號 - 分類應用
鐵達尼數據

1 | import seaborn as sns |
決策樹設計鐵達尼號預測

1 | import seaborn as sns |
交叉分析表格介紹
1 | import pandas as pd |
鐵達尼號交叉分析
1 | import seaborn as sns |
Telco 電信公司(from Kaggle) - 分類應用
數據內容


1 | import pandas as pd |
決策樹數據分析
1 | import pandas as pd |
了解特徵對模型的重要性
1 | import pandas as pd |
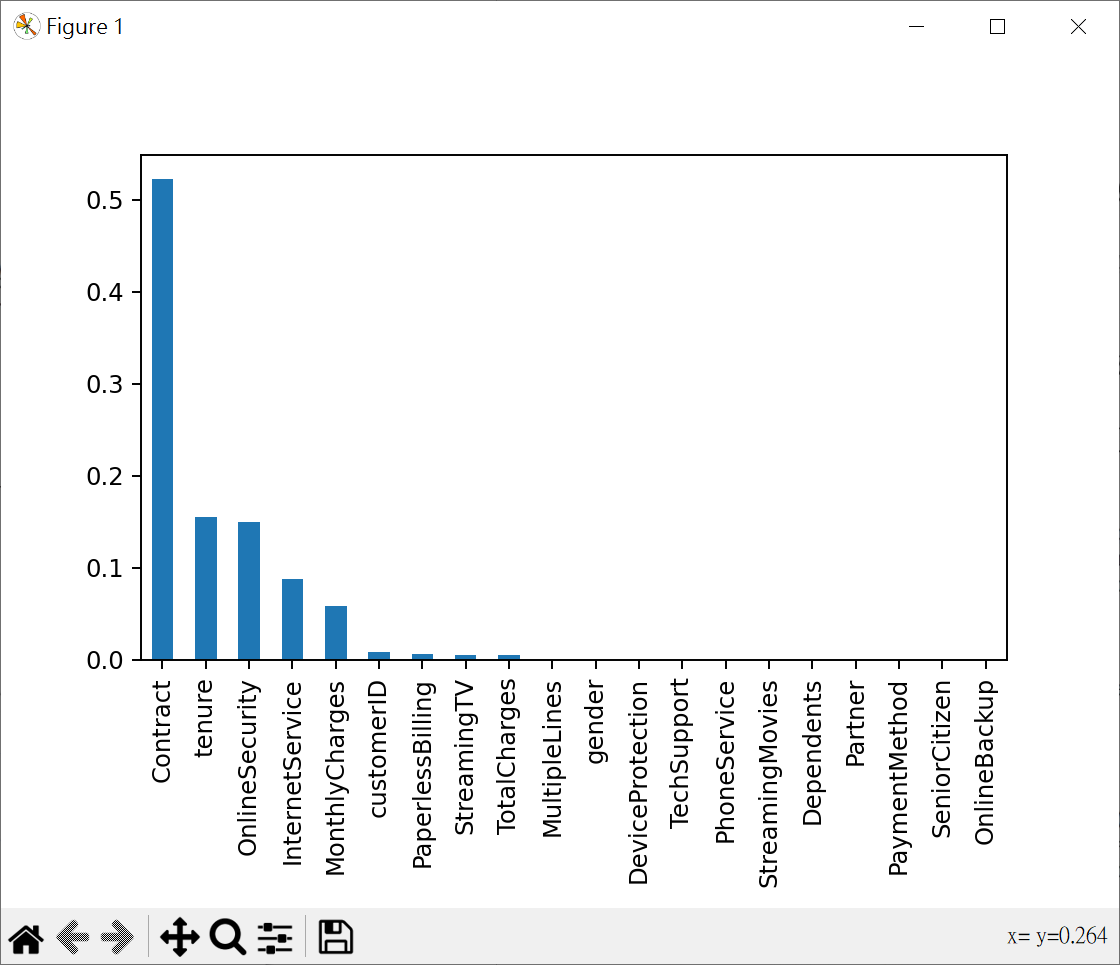
使用最重要5個特徵做決策樹數據分析
1 | import pandas as pd |
交叉驗證 - 決策樹最佳深度調整
GridSearchCV() 可用於有系統地遍歷多種參數組合

1 | import pandas as pd |
Retail Data Analytics - 迴歸應用
決策樹迴歸,可處理連續值(對比線性迴歸模型,更容易受到極端值的影響,並且可能在訓練數據不足下產生過度擬合)
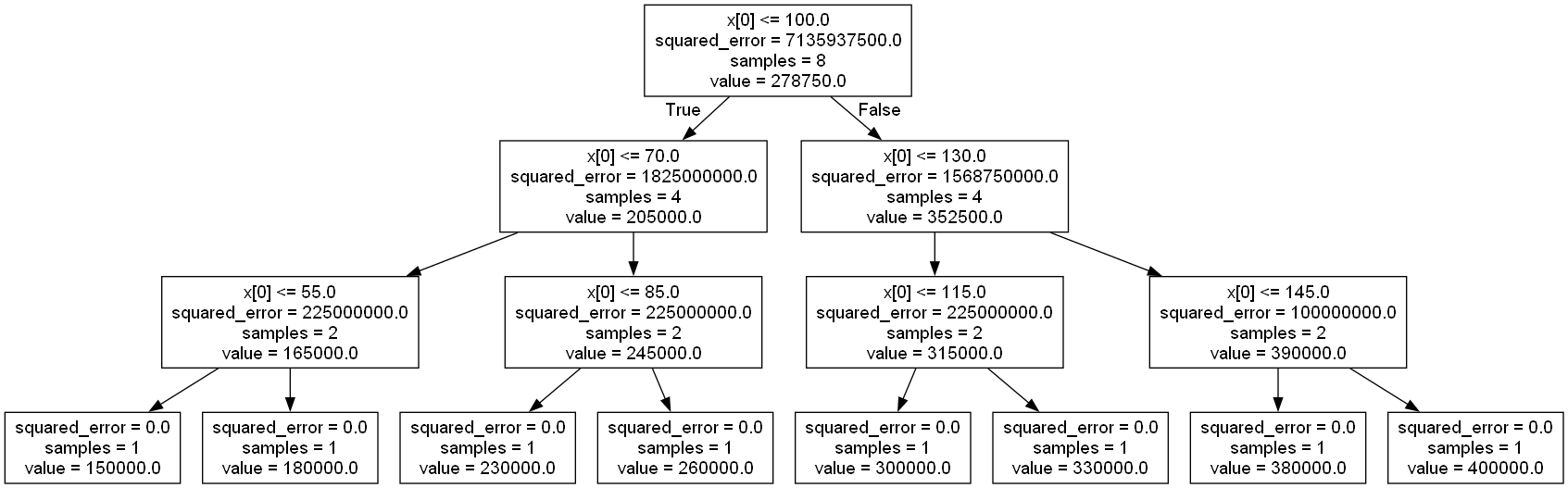
用簡單數據預估房價
1 | from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor |
Retail Data Analytics

1 | import pandas as pd |
隨機森林樹-波士頓房價,鐵達尼號,Telco,收入分析
決策樹簡單易懂,但資料若有變動常有不準的形況,隨機森林樹(Random Forest)是將一堆決策樹組織起來這樣可以獲得比較好的結果

波士頓房價 - 迴歸應用
簡單數據執行森林樹的應用
1 | # 簡單數據執行隨機森林(迴歸應用) |
波士頓房價森林樹的應用
得到比線性迴歸更好的R平方判定係數
1 | from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor |
鐵達尼號 - 分類應用
得到和決策樹相同的準確率
1 | import seaborn as sns |
Telco 客戶流失 - 分類應用
準確率差一點點
1 | import pandas as pd |
美國成年人收入分析(kaggle) - 分類應用
adult.csv 數據


1 | import pandas as pd |
使用決策樹處理年收入預估
1 | import pandas as pd |
特徵之重要性
1 | # 特徵之重要性 |
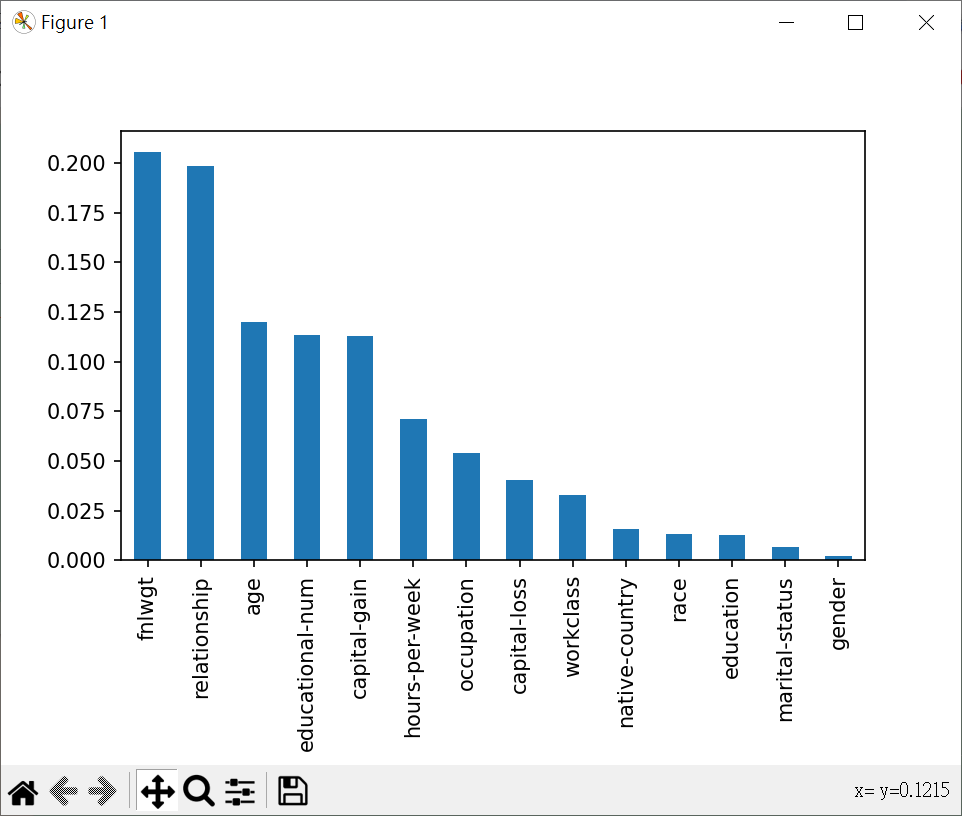
使用7個最重要特徵做決策樹處理年收入預估 - 並沒有比較好
1 | import pandas as pd |
使用隨機森林處理收入預估 - 得到較準確結果
1 | import pandas as pd |
KNN 演算法 - 鳶尾花,小行星撞地球
KNN(K-Nearest Neighbors K-最近鄰) 演算法基礎觀念

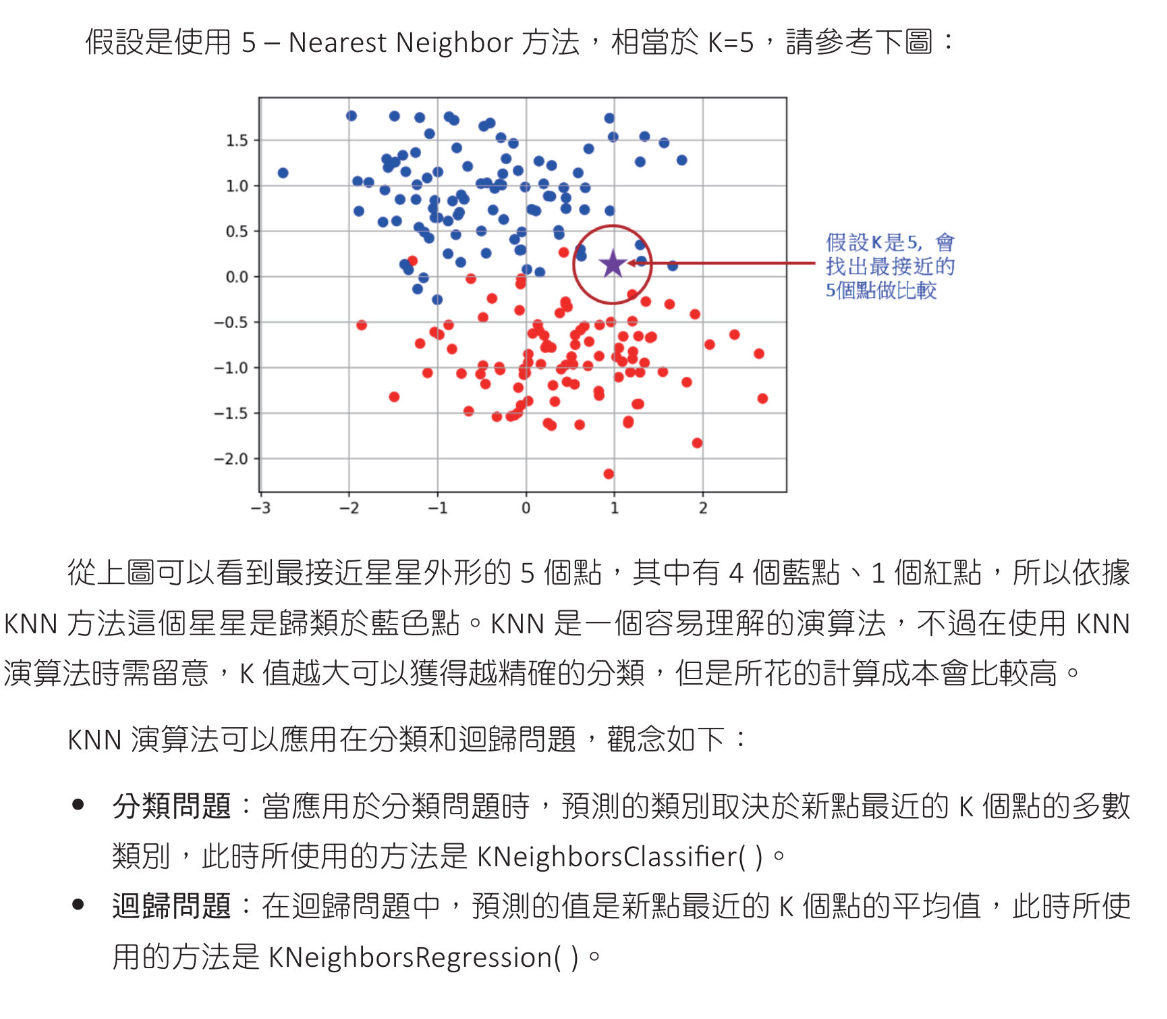
電影推薦,足球射門 - 分類應用
簡單例子
1 | # 簡單例子 |
電影推薦
1 | # 喜好電影預測 |
1 | # 喜好電影預測 |
足球進球分析
1 | # 足球進球分析 |
繪製分類決策邊界(ecision Boundary)
線性回歸數據集-繪製散點圖
1 | from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs |
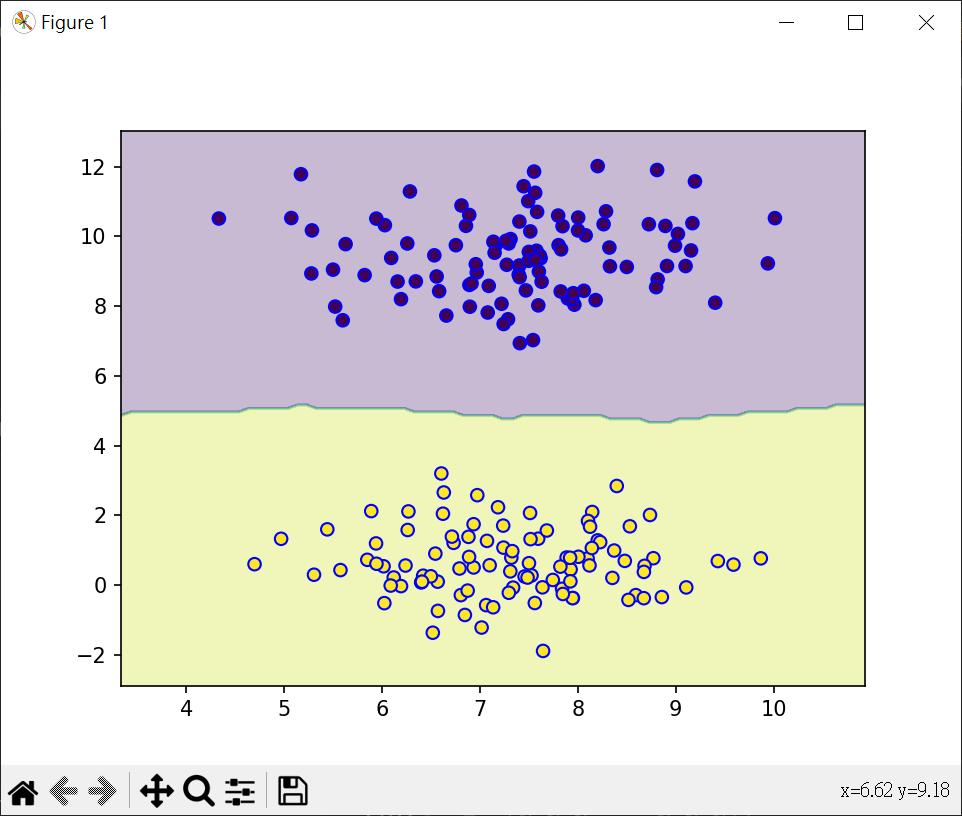
繪製分類邊界
1 | from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs |
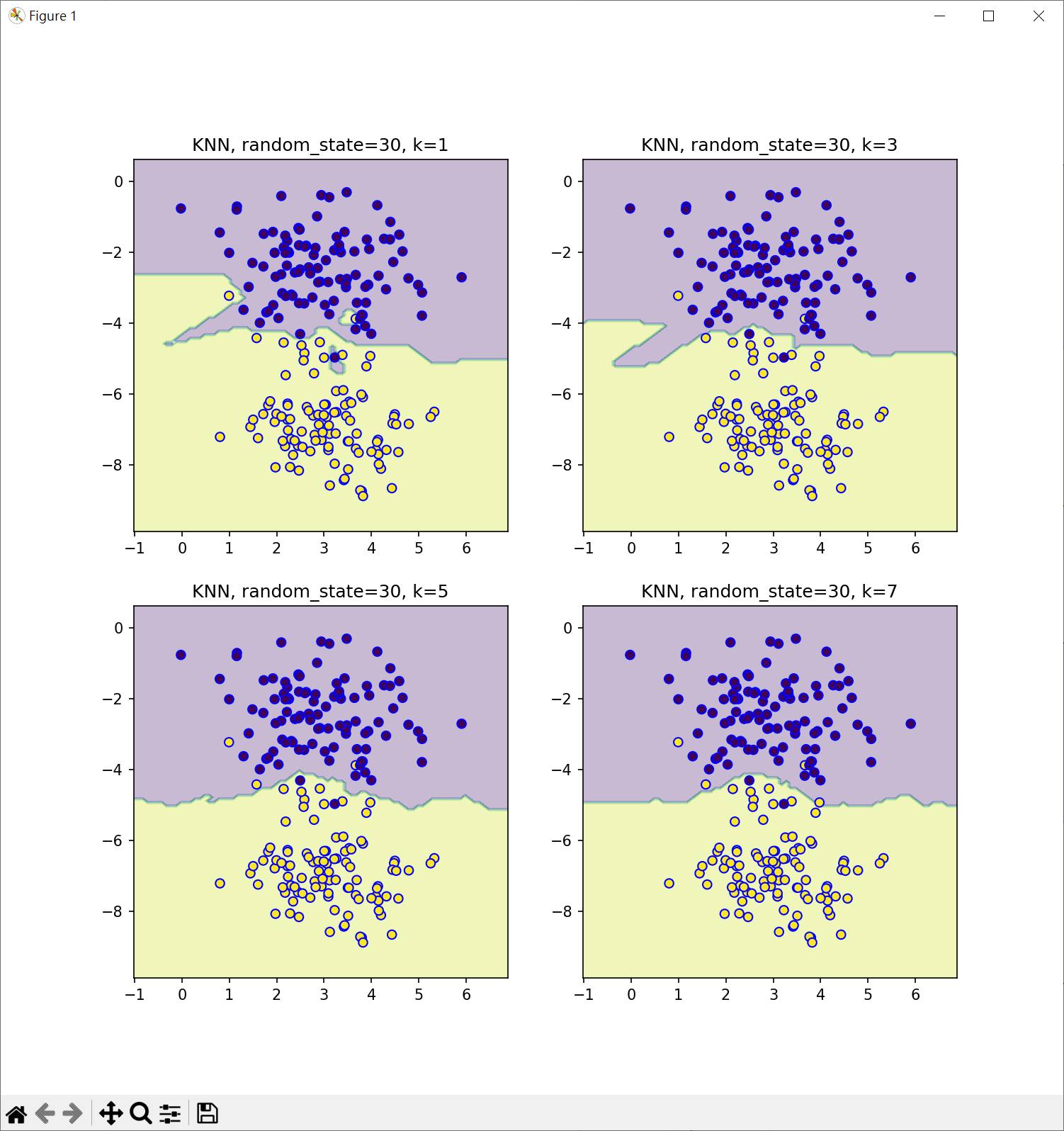
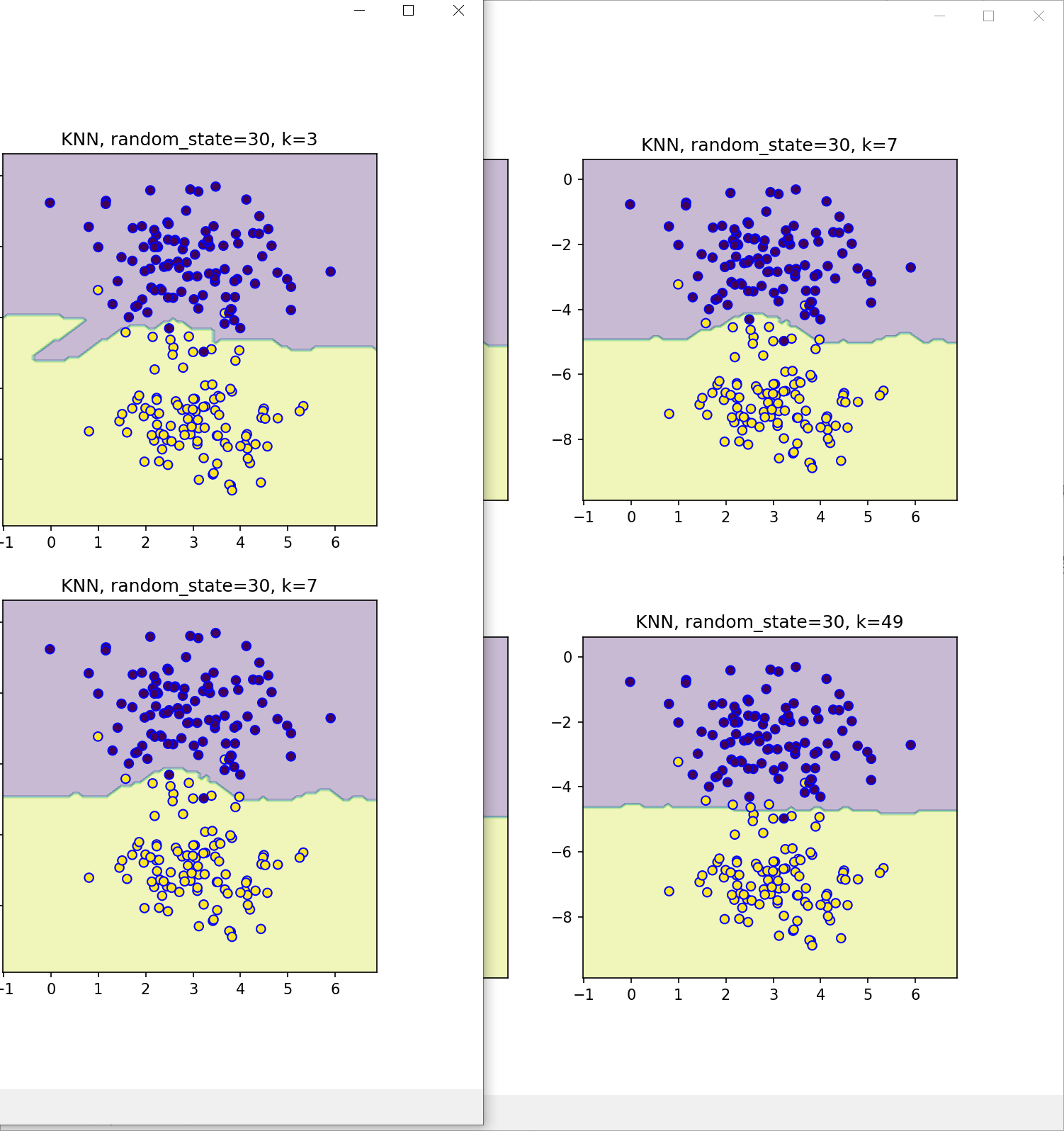
繪製分類邊界 - 調整隨機種子及k值
- k=1 會造成決策邊界對於異常值,錯誤標記值非常敏感
- k值放到很大時,會有欠擬合的問題
- KNN 演算法關鍵點就是找到k值,可以獲得最好的分類
- 欠擬合
- 低測試準確率
- 改進:調整 K 值,增加特徵,減少噪音(對數據進行清理和預處理),使用更複雜的模型
1 | from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs |
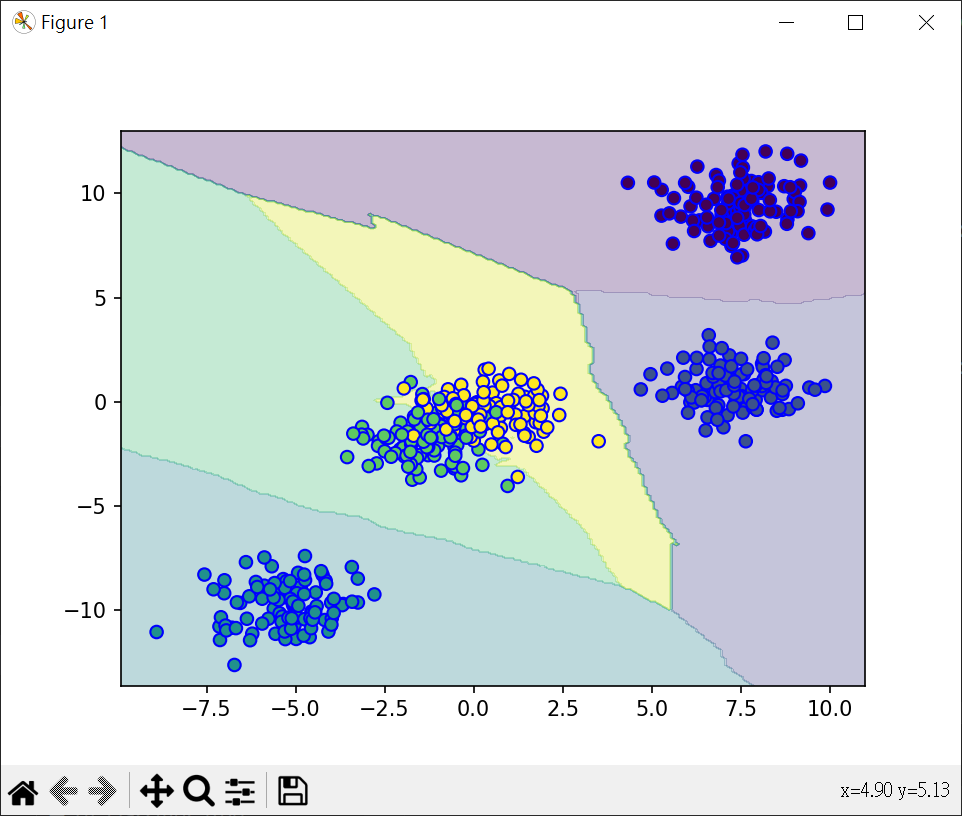
多類分析
錯誤原因應該是資料重疊,分成4類應較為適當
1 | from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs |
房價計算,選舉準備香腸 - 迴歸應用
KNN迴歸應用 - 簡單實例
1 | # KNN迴歸應用 - 簡單實例 |
KNN迴歸應用 - 房價預估
1 | # KNN迴歸應用 - 房價預估 |
1 | # KNN迴歸應用 - 房價預估2 |
選舉造勢與準備烤香腸數量
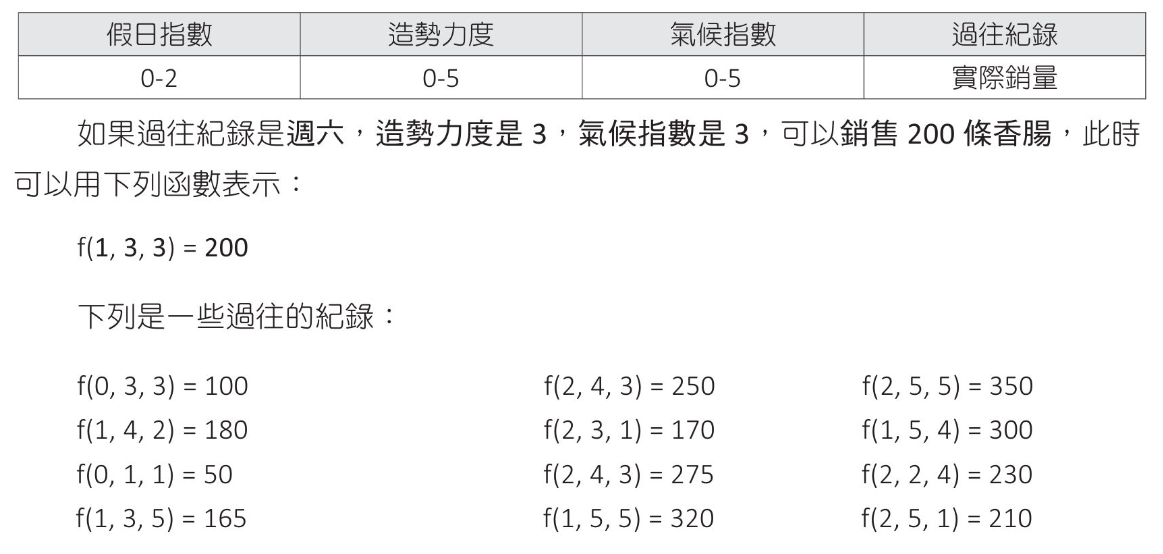
1 | # 造勢烤香腸預估 |
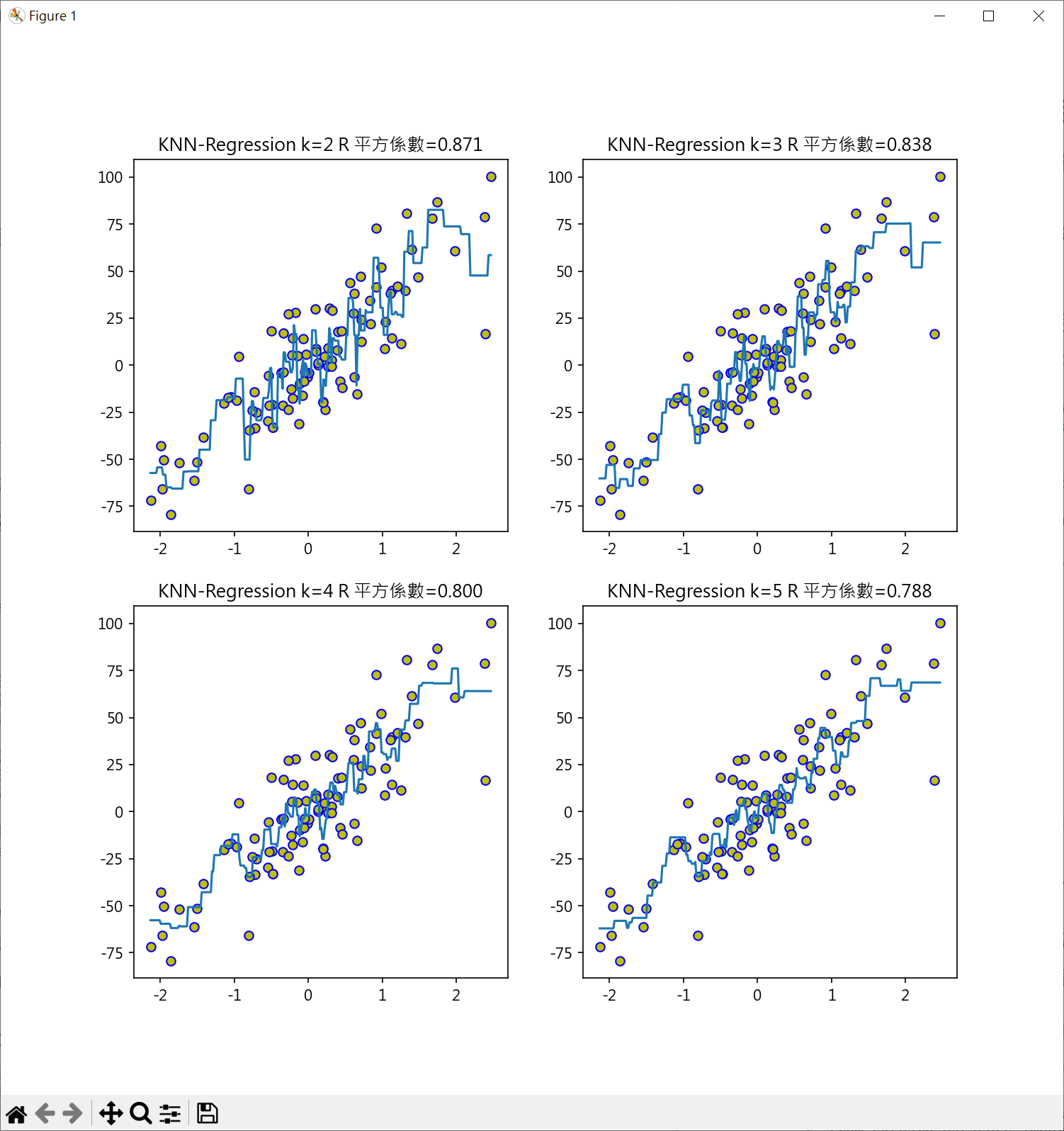
KKK 模型回歸線分析
繪製散點圖
1 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt |
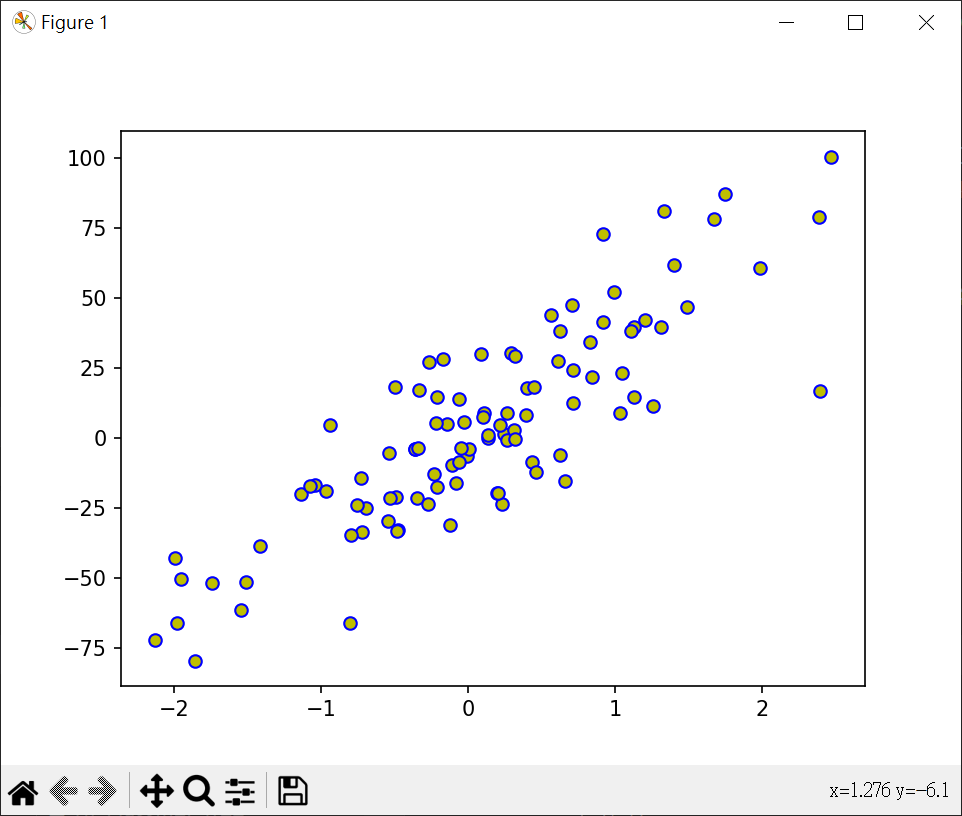
繪製KNN迴歸曲線
設定k值 2,3,4,5 同時計算 R平方判定係數,得到最好模型的k值
1 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt |
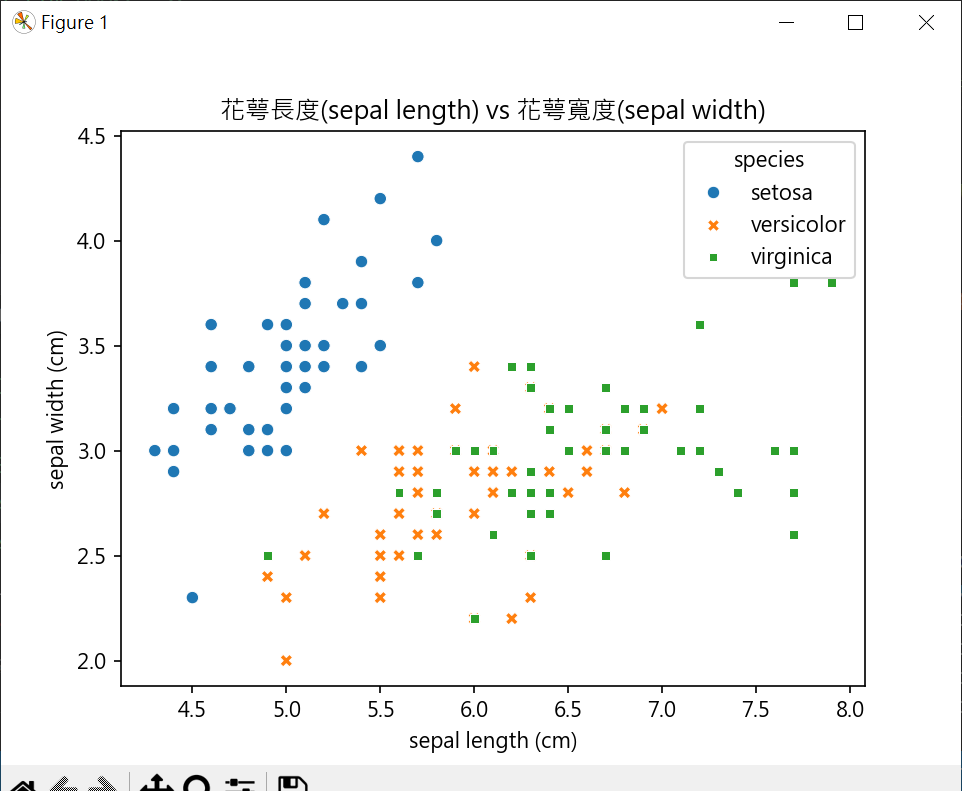
鳶尾花數據-分類應用
鳶尾花數據內容

輸出數據集

1 | from sklearn import datasets |
用 Pandas 顯示鳶尾花數據
1 | # pandas 顯示鳶尾花數據 |
繪製特徵散點圖
1 | from sklearn import datasets |
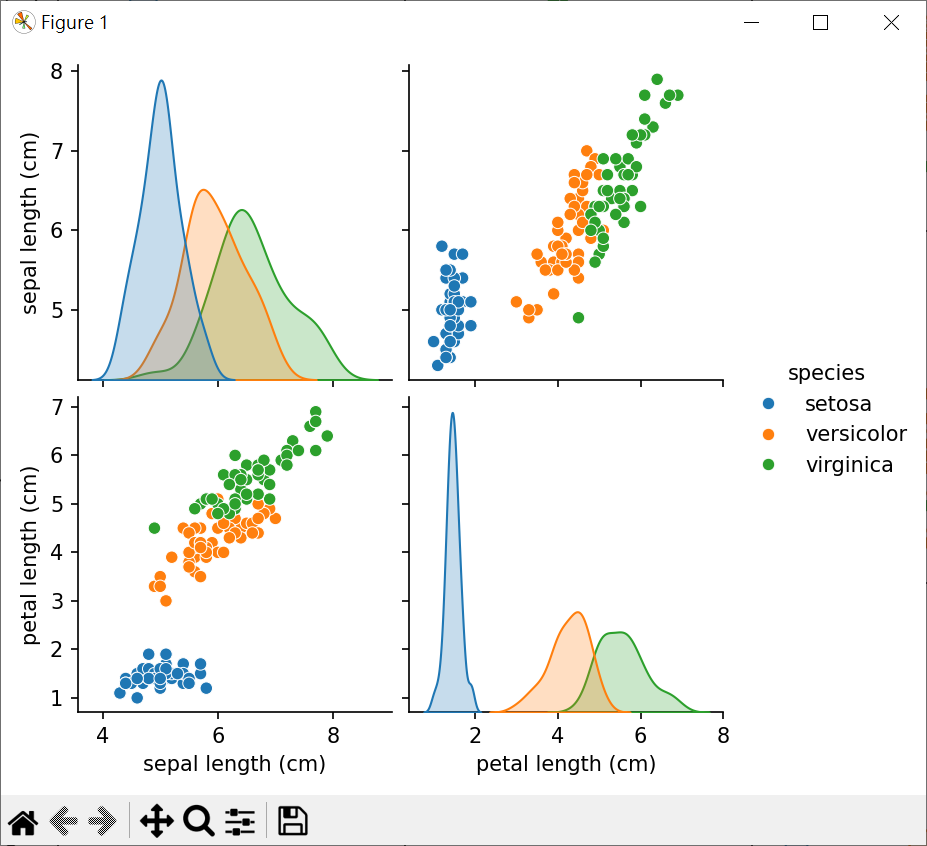
繪製成對數據特徵散點圖
1 | # 設計機器學習模型,繪製所有變數的散點圖,也是認識數據特徵的好方法 |
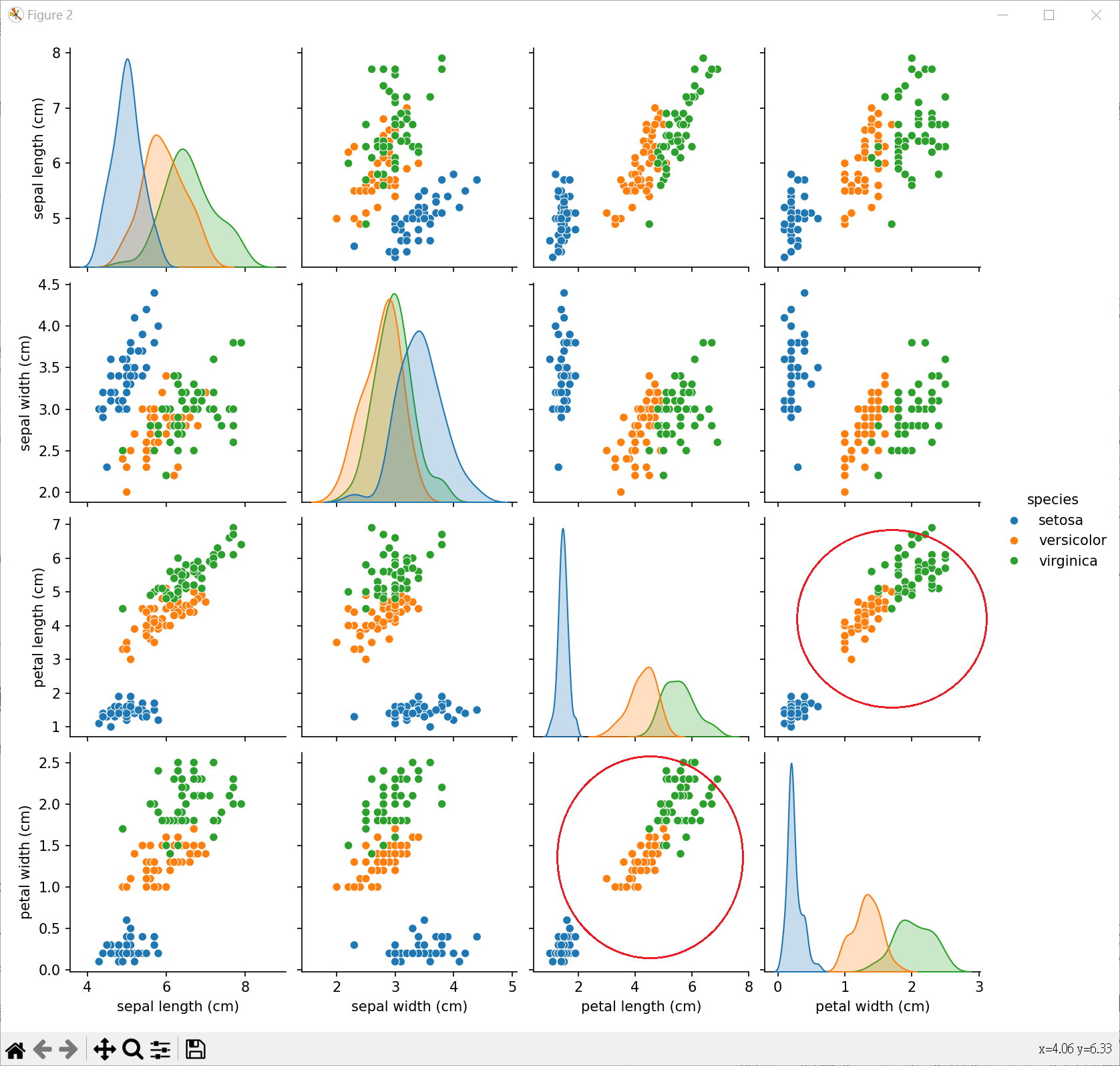
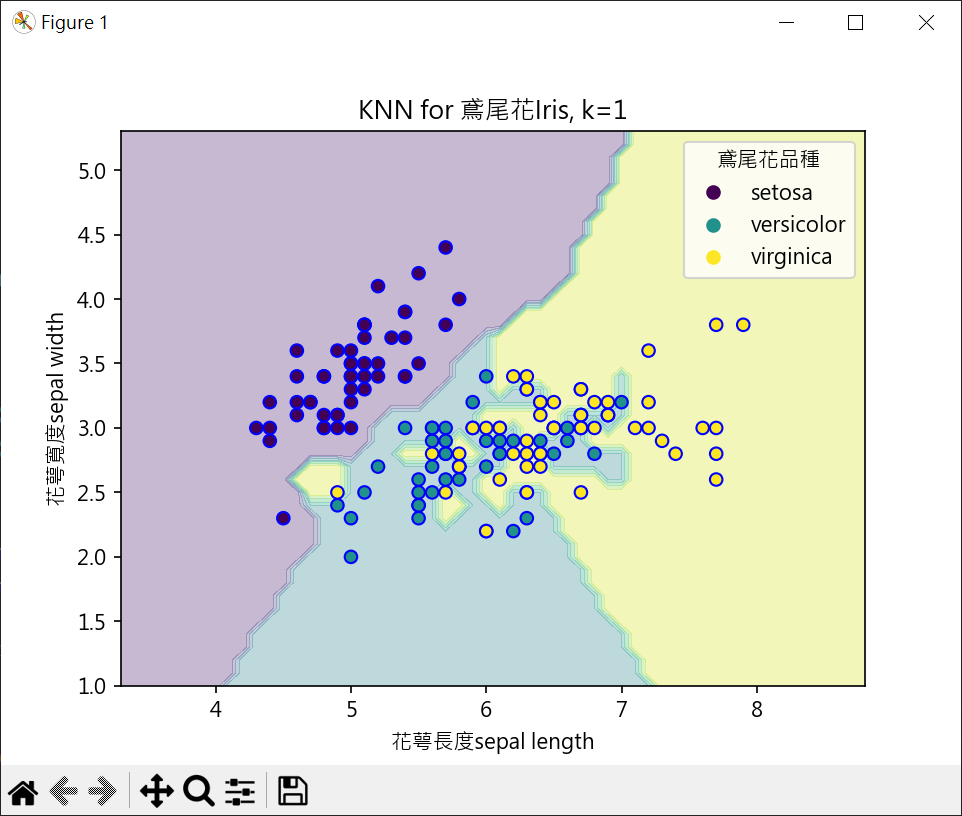
繪製鳶尾花決策邊界
1 | from sklearn import datasets |
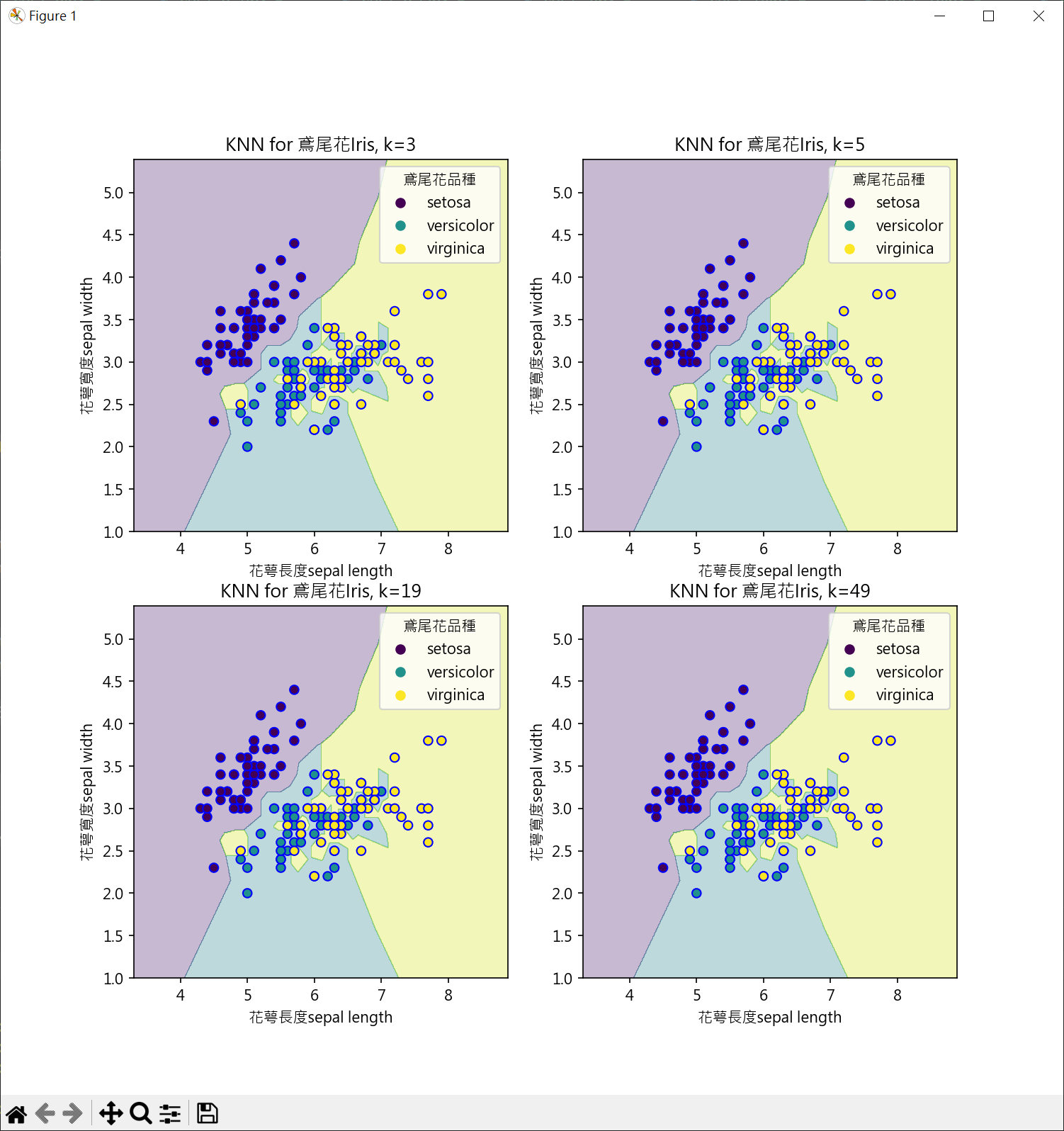
繪製鳶尾花決策邊界(不同k值)
1 | from sklearn import datasets |
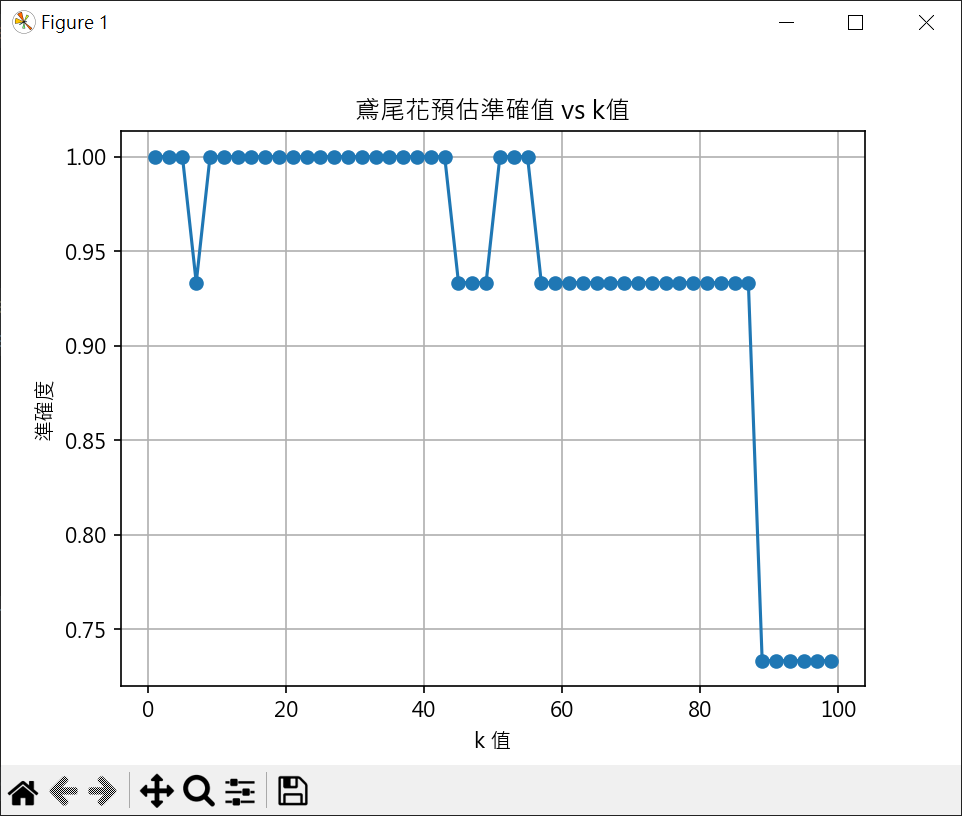
計算最優k值
k<43 有較好的準確度
1 | # 計算最優k值 (k<43 有較好的準確度) |
小行星撞地球-分類應用
Kaggle NANA ASteroids Classification 數據


1 | import pandas as pd |
預處理資料

1 | import pandas as pd |
預測小行星撞地球準確率
1 | import pandas as pd |