基本
scikit-learn 是一個開源的 python 機器學習庫,提供一系列監督及非監督學習算法
提供大量用於分類,迴歸,群集,降維,模型選擇和預處理工具
廣泛運用於數據挖掘和數據分析
install 1 pip install scikit-learn
評估模型 均方誤差(Mean Square Error, MSE) MSE是觀察值與預測值之間差值平方的平均值,MSE越小,表示模型的預測能力越好,公式如下
1 2 3 from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error ... MSE = mean_squared_error(y_true, y_pred)
均方根誤差(Root Mean Square Error, RMSE) 這是MSE的平方根,與MSE相比,RMSE對較大的誤差有更強的懲罰效果
平均絕對誤差(Mean Absolute Error, MAE) 這是預測值與實際值之間的絕對差平均值,這個指標能夠更好的反映預測誤差的實際大小
1 2 3 from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error ... MAE = mean_absolute_error(y_true, y_pred)
R平方判定係數(Coefficient of Determination RMSE) R平方判定係數或簡稱判定係數,是一個迴歸模型性能評估指標,用於衡量模型資料變異程度.值介於0~1,越接近1表示模型對資料的擬合程度越好.
$ Adjusted R^2 = 1 - \frac{(1-R^2)*(n-1)}{(n-k-1)} $
判定係數公式如下:
$ n 是數據量, \hat{y}_i 是迴歸函數的預估值,\overline{y} 是所有y的平均值 $
1 2 3 from sklearn.metrics import r2_score ... R2_score = r2_score(y_true, y_pred)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 from sklearn.metrics import r2_score, mean_squared_errorimport numpy as npx = [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 ,10 ,11 , 12 ,13 ,14 ,15 ,16 ,17 ,19 ,21 ,22 ,23 ,24 ] y = [100 , 88 , 75 , 60 , 50 , 55 , 55 , 56 , 58 , 58 , 61 , 63 , 68 , 71 , 71 , 75 , 76 , 88 , 93 , 97 , 97 , 100 ] coef = np.polyfit(x, y, 3 ) model = np.poly1d(coef) print (f"MSE:{mean_squared_error(y, model(x)):.3 f} " )print (f"R2_Score:{r2_score(y, model(x)):.3 f} " )
機器學習數據集 可使用以下數據集作為機器學習使用
scikit-learn 內建數據集 scikit-learn 提供一些數據集
鳶尾花 Iris
手寫數字 Digits
葡萄酒 Wine
威斯康辛州乳癌 Breast Cancer Wisconsin
波士頓房價 Boston House Prices
Kaggle 數據集
Kaggle 是一個數據科學平台
數據涵蓋許多不同主題,包含但不限於金融,醫療,影像識別,自然語言處理,音訊分析
Kaggle 有活躍的社區,你可以參加由Kaggle或其他機構主辦的數據科學競賽,並可以查看其他使用者對數據集的分析和模型
對每個數據集,可以找到相關的核心筆記本(kernels),討論和新聞,這些可幫助使用者理解和使用數據集
UCI 數據集
函數生成數據集(scikit-learn 函數生成數據) 也可以使用 scikit-learn 內建的函數生成下列類型的數據集:
scikit-learn 生成數據實作 線性分佈數據 1 2 3 from sklearn.datasets import make_regression ... X, y = make_regression(n_samples, n_features, noise, random_state)
n_samples : options,生成樣品數量, default 100
n_features : options,生成特徵數量, default 100
noise : option,加入高斯噪聲的標準差, default 0
random_state : option,隨機生成器的種子,加入此參數確保每次生成數據一致, default None(每次生成數據不同)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 from sklearn.datasets import make_regressionX, y = make_regression(n_features=1 , noise=0 , random_state=0 ) print ("X 的資料格式:" )print (type (X), len (X))print (f"陣列維度:{X.ndim} " )print (f"陣列外型:{X.shape} " )print (f"陣列大小:{X.size} " )print (f"前5個X的樣本:" )print (X[:5 ])print ("=" *70 )print ("y 的資料格式:" )print (type (y), len (y))print (f"陣列維度:{y.ndim} " )print (f"陣列外型:{y.shape} " )print (f"陣列大小:{y.size} " )print (f"前5個y的樣本:" )print (y[:5 ])
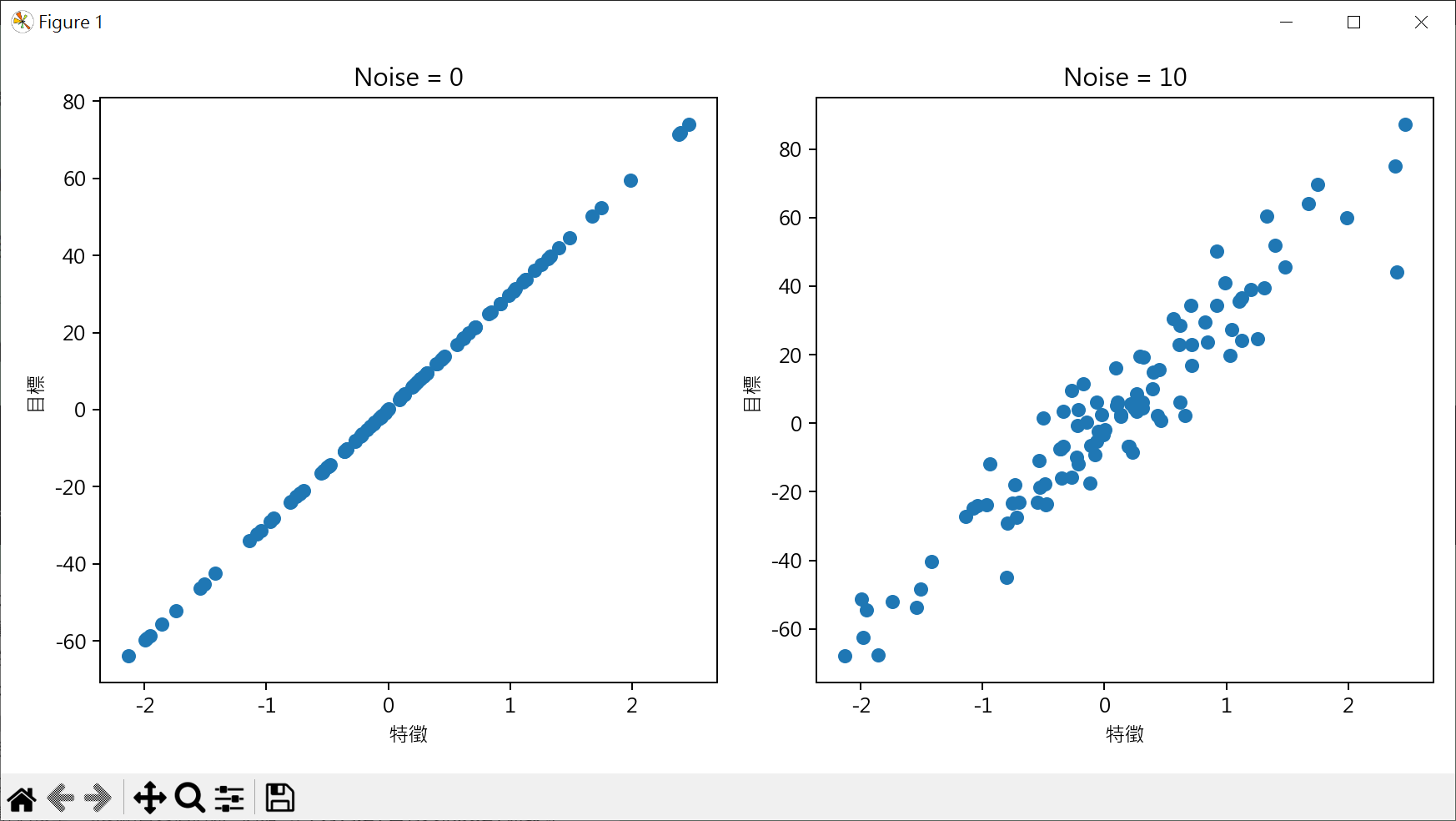
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 from sklearn.datasets import make_regressionimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltplt.rcParams["font.family" ] = ["Microsoft JhengHei" ] plt.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus" ] = False X1, y1 = make_regression(n_features=1 , noise=0 , random_state=10 ) X2, y2 = make_regression(n_features=1 , noise=10 , random_state=10 ) fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=1 , ncols=2 , figsize=(10 ,5 )) axs[0 ].scatter(X1, y1) axs[0 ].set_title("Noise = 0" ) axs[1 ].scatter(X2, y2) axs[1 ].set_title("Noise = 10" ) for ax in axs: ax.set_xlabel("特徵" ) ax.set_ylabel("目標" ) plt.tight_layout() plt.show()
群集分佈數據 1 2 3 from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs ... X,y = make_blobs(n_samples, n_features, centers, random_state)
n_samples : options,生成樣品數量, default 100
n_features : options,每個樣品特徵數, default 2
centers : option,整數或是一組[n_cneters, n_feature]的陣列,表示生成數據中心數量或固定中心位置, default 3
random_state : option,隨機生成器的種子,加入此參數確保每次生成數據一致, default None(每次生成數據不同)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 from sklearn.datasets import make_blobsX,y = make_blobs(n_samples=500 , n_features=2 , centers=5 , random_state=1 ) print (f"輸出 X 的資料格式:" )print (type (X))print (f"X 前 5 個樣本" )print (X[:5 ])print ("=" *70 )print (f"X[:,0] 前 5 個樣本" )xx = X[:,0 ] print (xx[:5 ])print ("=" *70 )print (f"X[:,1] 前 5 個樣本" )xx = X[:,1 ] print (xx[:5 ])print ("=" *70 )print (f"y 前 5 個樣本" )print (y[:5 ])
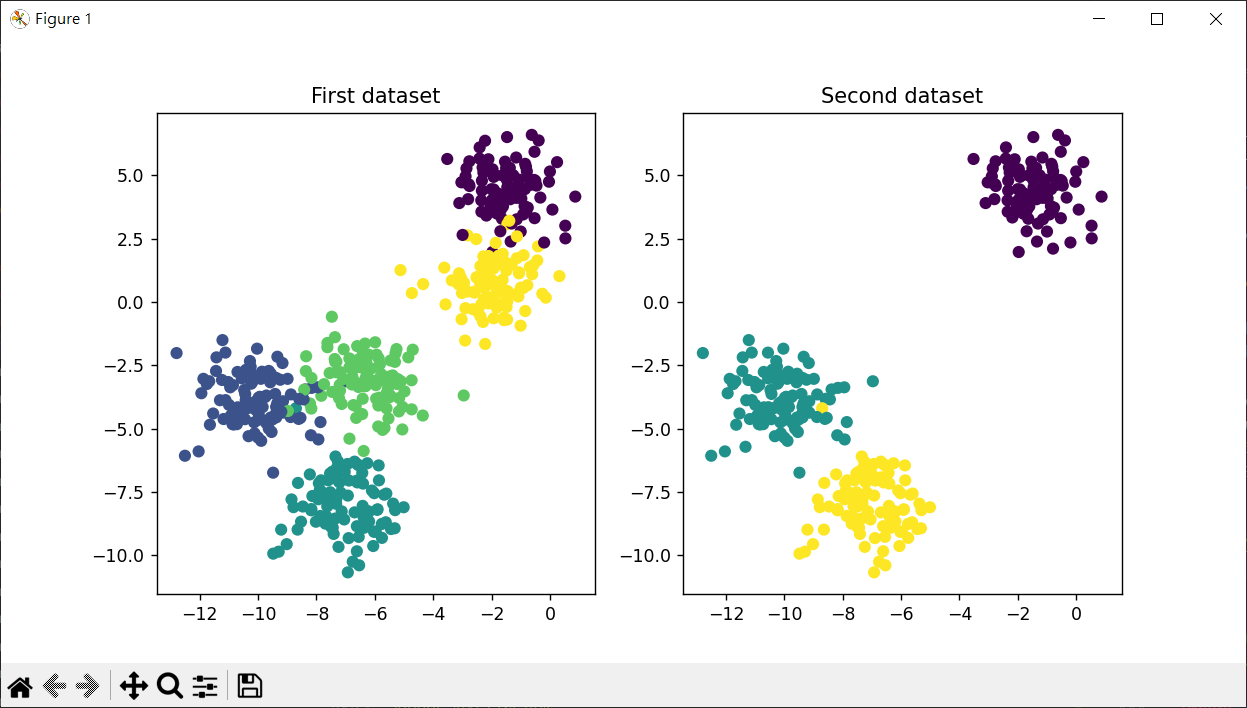
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 from sklearn.datasets import make_blobsimport matplotlib.pylab as pltX1 ,y1 = make_blobs(n_samples=500 , n_features=2 , centers=5 , random_state=1 ) X2 ,y2 = make_blobs(n_samples=300 , n_features=2 , centers=3 , random_state=1 ) fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=1 , ncols=2 , figsize=(10 ,5 )) axs[0 ].scatter(X1[:,0 ], X1[:,1 ], c=y1) axs[0 ].set_title("First dataset" ) axs[1 ].scatter(X2[:,0 ], X2[:,1 ], c=y2) axs[1 ].set_title("Second dataset" ) plt.show()
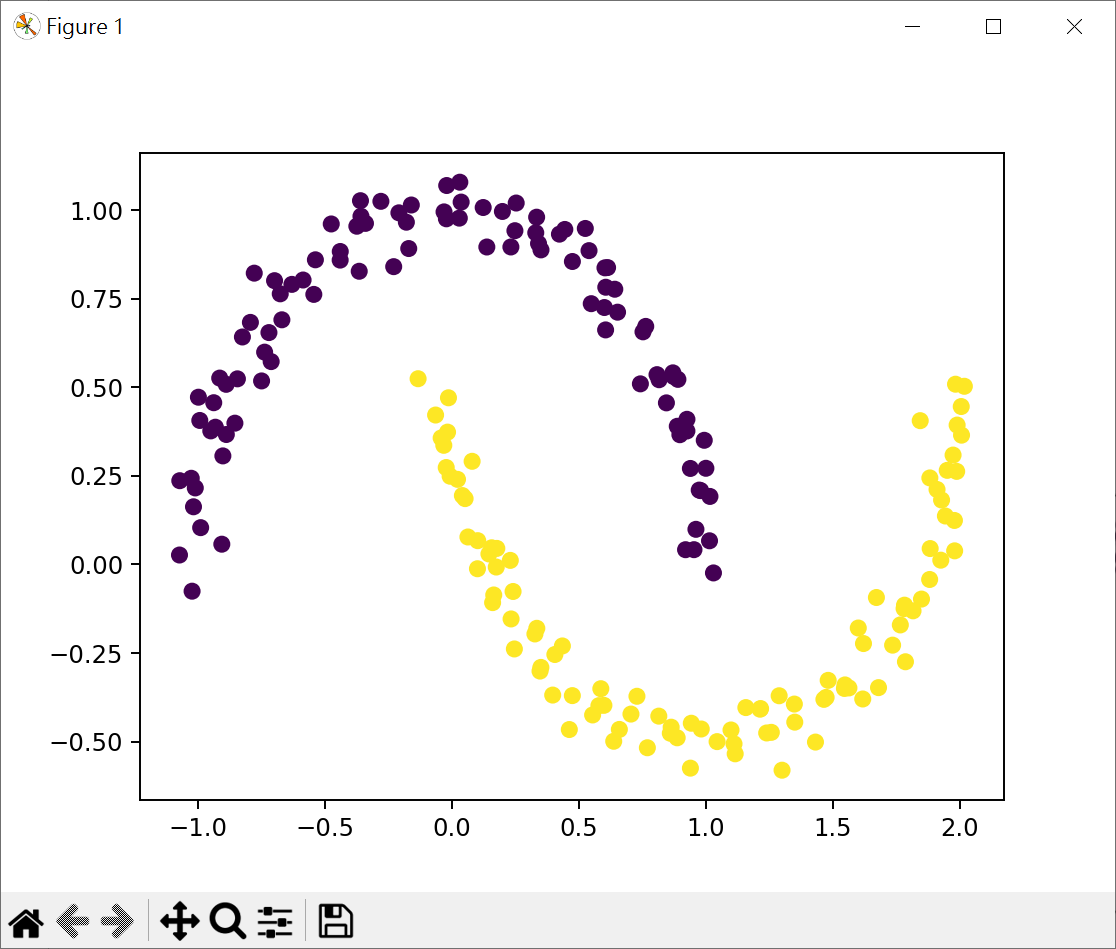
交錯半月群集數據 玩具數據集通常指那些簡單,小型的人造數據集
1 2 3 from sklearn.datasets import make_moons ... X, y = make_moons(n_samples, noise, random_state)
n_samples : options,生成樣品數量, default 100
noise : option,加入高斯噪聲的標準差, default None
random_state : option,隨機生成器的種子,加入此參數確保每次生成數據一致, default None(每次生成數據不同)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 from sklearn.datasets import make_moonsimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltX, y = make_moons(n_samples=200 , noise=0.05 , random_state=0 ) print (f"X[:5] = {X[:5 ]} " )print (f"y={y} " )plt.scatter(X[:,0 ], X[:,1 ], c=y) plt.show()
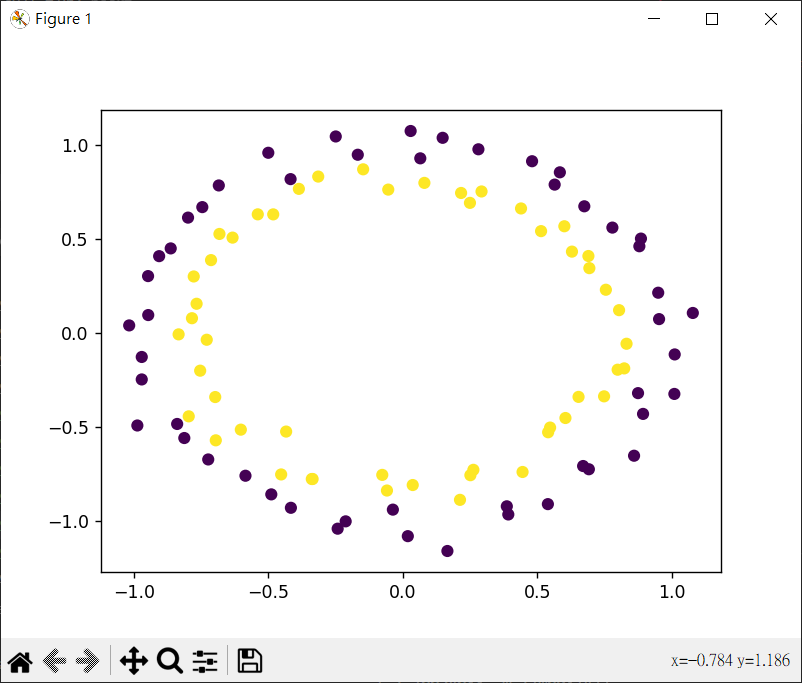
環形結構分佈的群集數據 make_circles() 可以用來生成兩個環狀結構的數據集,一個圓內部的點和一個圓外部的點
1 2 3 from sklearn.datasets import make_circles ... X, y = make_circles(n_samples, noise, random_state)
n_samples : options,生成樣品數量, default 100
noise : option,加入高斯噪聲的標準差, default None
random_state : option,隨機生成器的種子,加入此參數確保每次生成數據一致, default None(每次生成數據不同)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 from sklearn.datasets import make_circlesimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltX, y = make_circles(n_samples=100 , noise=0.05 , random_state=0 ) plt.scatter(X[:,0 ], X[:,1 ], c=y) plt.show()
n-class 分類數據集 1 2 3 from sklearn.datasets import make_classification ... X, y = make_classification(n_samples=100 , n_features=20 , n_informative=2 , n_redundant=2 , n_repeated=0 , n_classes=2 , n_clusters_per_class=2 , weights=None , hypercube=True , shift=0.0 , scale=1.0 , shuffle=True , random_state=None )
n_samples : options,生成樣品數量, default 100
n_features : options,生成特徵數量, default 20
n_informative : 信息特徵數, default 2
n_redundant : 冗餘特徵數, default 1
n_repeated : 重複特徵數, default 0
n_classes : 數據集中類別數, default 2
n_clusters_per_class : 每個類別的簇數, default 2
weights : 每個類別樣品所佔的比例, default None
hypercube : 如為 True 將簇放置在超立方體的頂點上, 如為 False 將簇放置在隨機多維標準常規中, default True
shift : 特徵的均值, default 0.0
scale : 特徵的標準差, default 1.0
random_state : option,隨機生成器的種子,加入此參數確保每次生成數據一致, default None(每次生成數據不同)
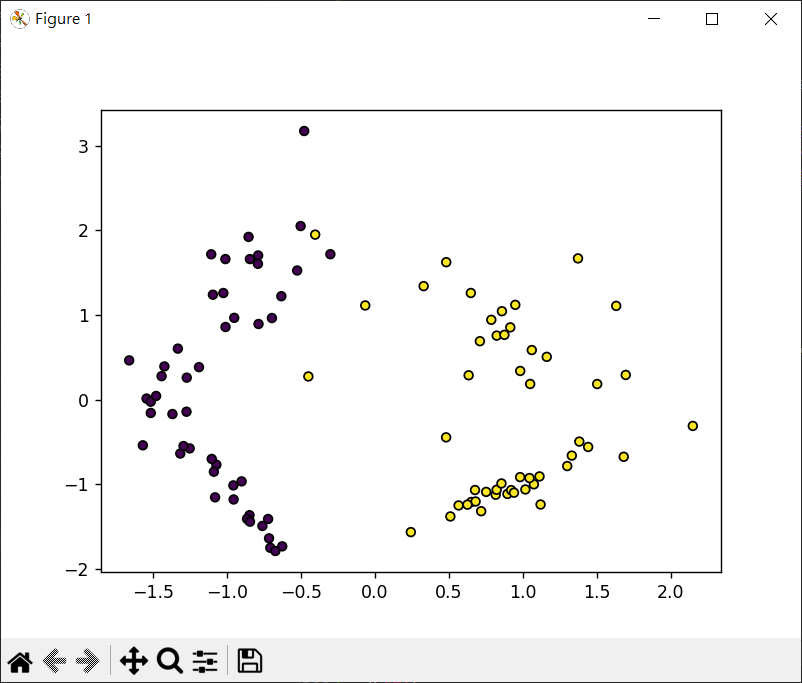
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 from sklearn.datasets import make_classificationimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltX, y = make_classification(n_samples=100 , n_features=2 , n_informative=2 , n_redundant=0 , n_repeated=0 , n_classes=2 , random_state=1 ) plt.scatter(X[:,0 ], X[:,1 ], marker='o' , c=y, s=25 , edgecolors='k' ) plt.show()
scikit-learn 數據預處理 scikit-learn 數據預處理 有以下幾點
數據清洗:消除數據中的噪聲,例如遺漏值,異常值或不一致的數據等
數據轉換:將數據轉換成適合模型學習的格式.如某些算法只能處理數值數據,所以我們需要將類別數據進行編碼
數據標準化/正規化:消除數據尺度的差異,讓所有的特徵都在尺度範圍內(數據標準化也稱為數據縮放)
特徵選擇/提取:有時我們要減少數據的維度以減少運算,或者將原始特徵轉換成更好表示數據的新特徵
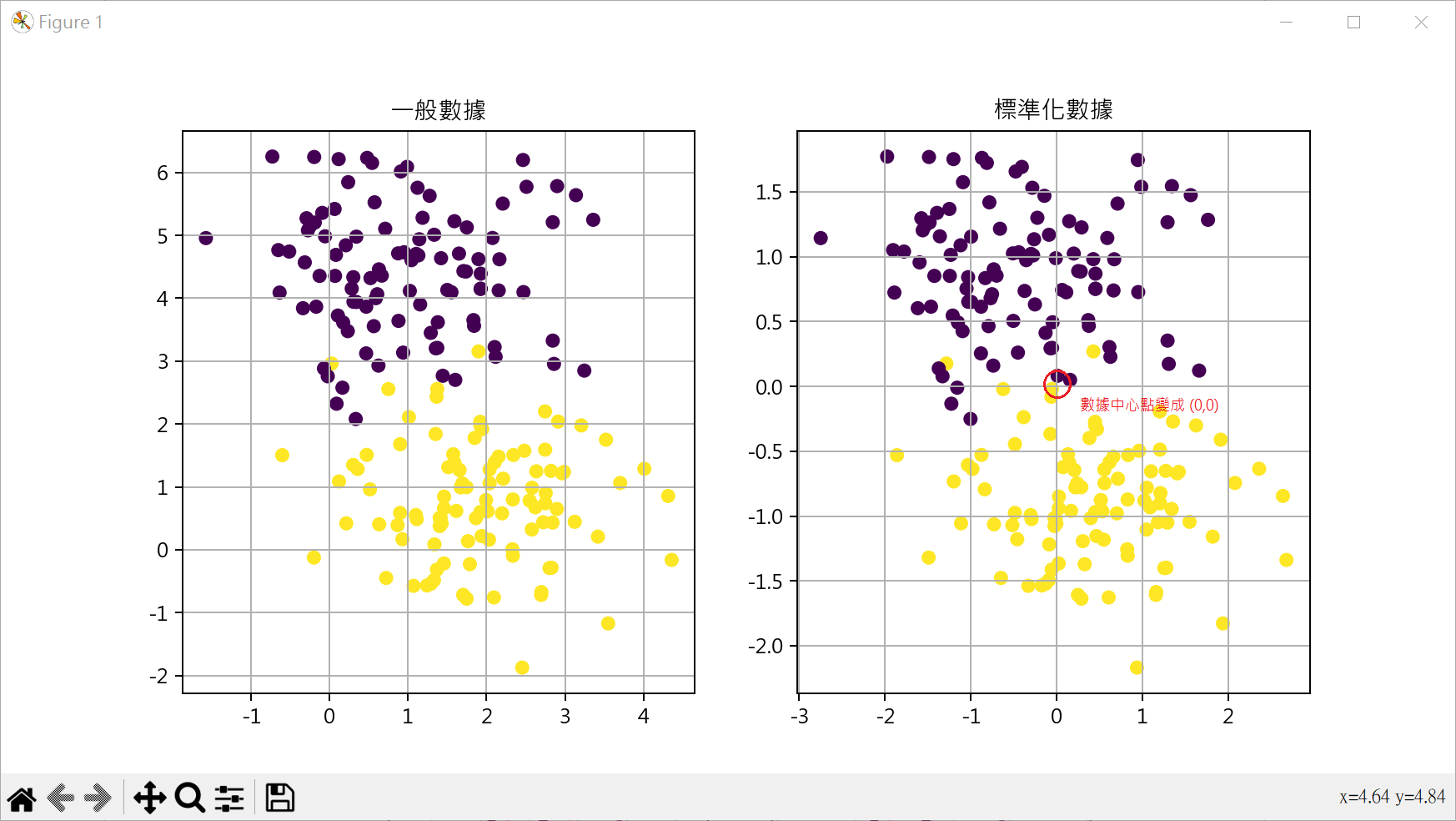
標準化數據 StandardScaler 有時使用 make_blobs()產生的數據,特徵資料的差異會很大,可使用StandardScaler()將資料標準化為平均數是0,變異數是1
1 2 3 from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler ... StandardScaler().fit_transform(data)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 from sklearn.datasets import make_blobsfrom sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScalerimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltplt.rcParams["font.family" ] = ["Microsoft JhengHei" ] plt.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus" ] = False X, y = make_blobs(n_samples=200 , n_features=2 , centers=2 , random_state=0 ) X_sta = StandardScaler().fit_transform(X) fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=1 , ncols=2 , figsize=(10 ,5 )) axs[0 ].scatter(X[:,0 ], X[:,1 ], c=y) axs[0 ].set_title("一般數據" ) axs[0 ].grid() axs[1 ].scatter(X_sta[:,0 ], X_sta[:,1 ], c=y) axs[1 ].set_title("標準化數據" ) axs[1 ].grid() plt.show()
設定數據區間 MinMaxScaler MinMaxScaler() 主要將資料縮放的最小值和最大值之間,通常是0到1,也可以是其他任意範圍
1 2 3 from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler ... MinMaxScaler().fit_transform(data)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 from sklearn.datasets import make_blobsfrom sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScalerimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltplt.rcParams["font.family" ] = ["Microsoft JhengHei" ] plt.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus" ] = False X, y = make_blobs(n_samples=200 , n_features=2 , centers=2 , random_state=0 ) X_sta = MinMaxScaler().fit_transform(X) fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=1 , ncols=2 , figsize=(10 ,5 )) axs[0 ].scatter(X[:,0 ], X[:,1 ], c=y) axs[0 ].set_title("一般數據" ) axs[0 ].grid() axs[1 ].scatter(X_sta[:,0 ], X_sta[:,1 ], c=y) axs[1 ].set_title("縮放0和1之間數據" ) axs[1 ].grid() plt.show()
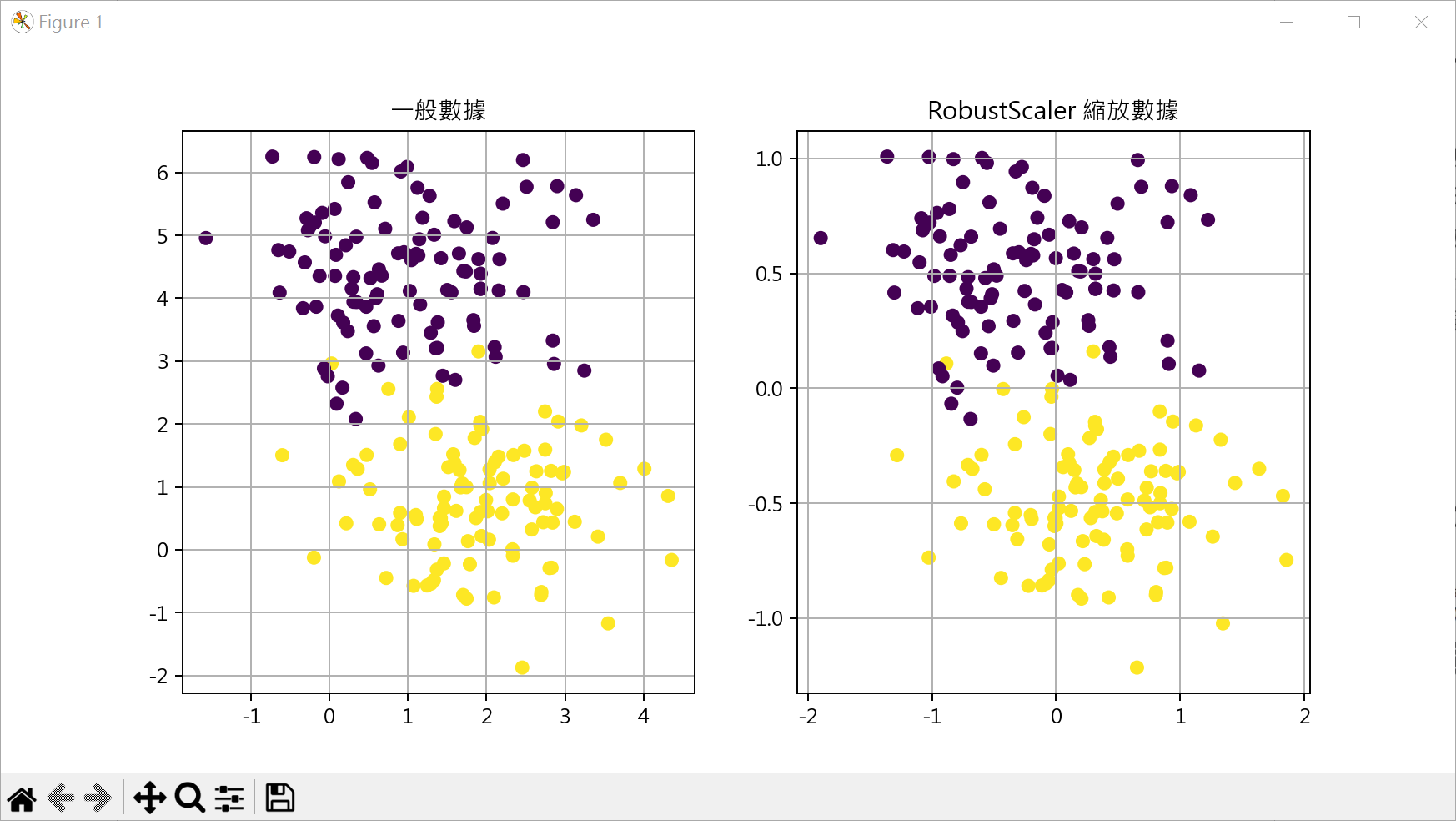
特殊數據縮放 RobusterScaler RobusterScaler()是一種特殊數據縮放器,特別適合處理含有異常的數據
1 2 3 from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaRobusterScalerxScaler ... RobusterScaler().fit_transform(data)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 from sklearn.datasets import make_blobsfrom sklearn.preprocessing import RobustScalerimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltplt.rcParams["font.family" ] = ["Microsoft JhengHei" ] plt.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus" ] = False X, y = make_blobs(n_samples=200 , n_features=2 , centers=2 , random_state=0 ) X_sta = RobustScaler().fit_transform(X) fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=1 , ncols=2 , figsize=(10 ,5 )) axs[0 ].scatter(X[:,0 ], X[:,1 ], c=y) axs[0 ].set_title("一般數據" ) axs[0 ].grid() axs[1 ].scatter(X_sta[:,0 ], X_sta[:,1 ], c=y) axs[1 ].set_title("RobustScaler 縮放數據" ) axs[1 ].grid() plt.show()
機器學習 scikit-learn 入門 使用 scikit-learn LinearRegression 建立線性回歸模型 1 2 3 4 5 6 from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegressionmodel = LinearRegression() model.fit(X, y)
model.predict(height) : 預測新數據
model.score(X_test, Y_test) : 獲得(X_test, Y_test)數據的R平方值
model.intercept_ : 模型方程式的截距
model.coef_ : 模型方程式的迴歸係數
X 必需為二維陣列,可使用 reshape(-1,1) 將一維轉為二維陣列
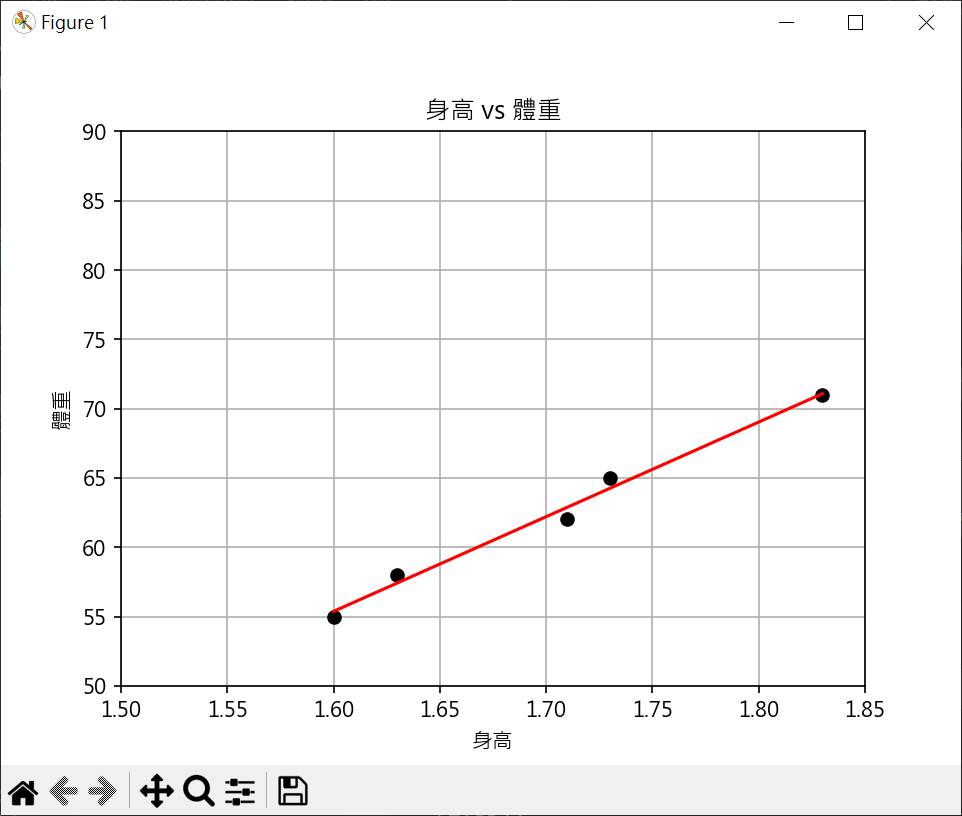
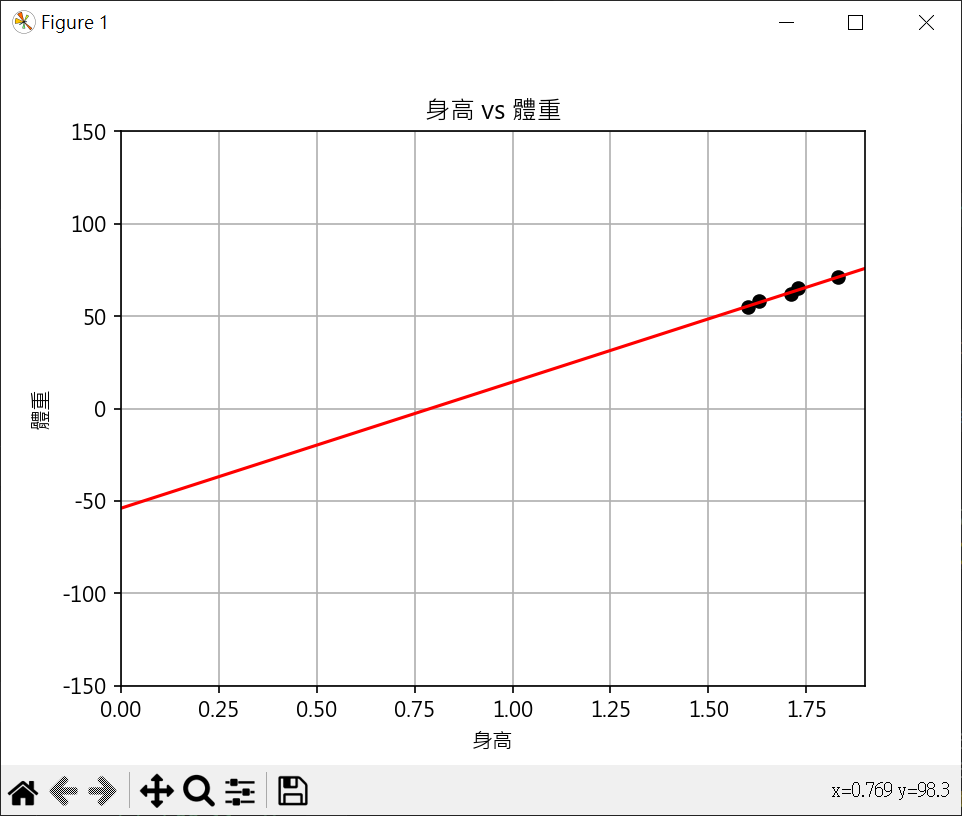
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 import matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegressionimport numpy as npplt.rcParams["font.family" ] = ["Microsoft JhengHei" ] height = np.array([1.6 , 1.63 , 1.71 , 1.73 , 1.83 ]).reshape(-1 ,1 ) weight = np.array([55 , 58 , 62 , 65 , 71 ]) plt.plot(height, weight, "ko" ) plt.axis([1.5 , 1.85 , 50 , 90 ]) plt.title("身高 vs 體重" ) plt.xlabel("身高" ) plt.ylabel("體重" ) print (f"height={height} " )print (f"height[:,0]={height[:,0 ]} " )coef = np.polyfit(height[:,0 ], weight, 1 ) reg = np.poly1d(coef) print (f"reg(height[:,0]) = {reg(height[:,0 ])} " )model = LinearRegression() model.fit(X=height, y=weight) y_pred = model.predict(height) plt.plot(height, y_pred, c='r' ) print (f"y_pred={y_pred} " )plt.grid() plt.show()
資料預測 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegressionimport numpy as npheight = np.array([1.6 , 1.63 , 1.71 , 1.73 , 1.83 ]).reshape(-1 ,1 ) weight = np.array([55 , 58 , 62 , 65 , 71 ]) model = LinearRegression() model.fit(X=height, y=weight) h = int (input ("輸入身高(cm):" )) h /= 100 weight_pred = model.predict([[h]]) print (weight_pred)print (f"預測體重: {weight_pred[0 ]:.2 f} 公斤" )
模型的儲存與載入 pickle 1 2 3 4 import picklepickle.dump(model, save_file) model = pickle.load(load_file)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 import picklefrom sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegressionimport numpy as npheight = np.array([1.6 , 1.63 , 1.71 , 1.73 , 1.83 ]).reshape(-1 ,1 ) weight = np.array([55 , 58 , 62 , 65 , 71 ]) model = LinearRegression() model.fit(X=height, y=weight) with open ("model_ch22_9.pkl" , "wb" ) as f: pickle.dump(model, f)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 import picklewith open ('model_ch22_9.pkl' , "rb" ) as f: model = pickle.load(f) h = int (input ("輸入身高(cm):" )) h /= 100 weight_pred = model.predict([[h]]) print (weight_pred)print (f"預測體重: {weight_pred[0 ]:.2 f} 公斤" )
joblib (scikit-learn 建議,可有較好的效率) 1 2 3 4 5 from joblib import dumpfrom joblib import loaddump(model, "model_name.joblib" ) model = load("model_name.joblib" )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 from joblib import dumpfrom sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegressionimport numpy as npheight = np.array([1.6 , 1.63 , 1.71 , 1.73 , 1.83 ]).reshape(-1 ,1 ) weight = np.array([55 , 58 , 62 , 65 , 71 ]) model = LinearRegression() model.fit(X=height, y=weight) dump(model, "model_ch22_11.joblib" )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 from joblib import loadmodel = load("model_ch22_11.joblib" ) h = int (input ("輸入身高(cm):" )) h /= 100 weight_pred = model.predict([[h]]) print (weight_pred)print (f"預測體重: {weight_pred[0 ]:.2 f} 公斤" )
計算線性迴歸線的斜率和截距 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 import matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegressionimport numpy as npplt.rcParams["font.family" ] = ["Microsoft JhengHei" ] plt.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus" ] = False height = np.array([1.6 , 1.63 , 1.71 , 1.73 , 1.83 ]).reshape(-1 ,1 ) weight = np.array([55 , 58 , 62 , 65 , 71 ]) plt.plot(height, weight, "ko" ) plt.axis([0 , 1.9 , -150 , 150 ]) plt.title("身高 vs 體重" ) plt.xlabel("身高" ) plt.ylabel("體重" ) model = LinearRegression() model.fit(X=height, y=weight) x_line = np.array([0 , 1.9 ]).reshape(-1 ,1 ) y_pred = model.predict(x_line) plt.plot(x_line, y_pred, c='r' ) print (f"y截距 : {model.intercept_:.2 f} " )print (f"斜率 : {model.coef_[0 ]:.2 f} " )plt.grid() plt.show()
R平方係數判定檢驗模型的性能 $ R^2(y,\hat{y}) = 1 - \frac{\sum_{i=1}^{n}(y_i - \hat{y}_i)^2} { \sum _{i=1}^{n}(y_i - \overline{y})^2 } = 1 - \frac{RSS}{TSS}$
RSS : Residual Sum of Squares,又稱為殘差平方和(或誤差平方和),表示模型無法解釋的變異性,RSS應盡可能小
TSS : Total of Squares,又稱為總平方和,衡量目標變數的變異性,表示目標變數的總變異性,TSS是模型預測值和實際值差異的上限
R 平方係數應盡可能接近 1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegressionimport numpy as npfrom sklearn.metrics import r2_scoreheight = np.array([1.6 , 1.63 , 1.71 , 1.73 , 1.83 ]).reshape(-1 ,1 ) weight = np.array([55 , 58 , 62 , 65 , 71 ]) model = LinearRegression() model.fit(X=height, y=weight) RSS = np.sum ((weight - np.ravel(model.predict(height))) ** 2 ) print (f"RSS : {RSS:.2 f} " )mean_weight = np.mean(weight) TSS = np.sum ((weight - mean_weight) ** 2 ) print (f"TSS : {TSS:.2 f} " )R_quare = 1 - (RSS/TSS) print (f"手工計算 R平方係數 : {R_quare:.2 f} " )R_score = model.score(height, weight) print (f"函數計算 R平方係數 : {R_score:.2 f} " )
分類演算法 - 機器學習模型的性能評估 計算精確度 accuracy_score() 計算分類器的準確度
1 2 3 from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score ... accuracy_score(y_true, y_pred, normalize=True , sample_weight=None )
y_true : 真實目標值陣列
y_pred : 模型預測值
normalize : True(default)返回正確比例, Flase返回正確分類總數
sample_weight : option,可提供各個權重
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_scorey_true = [1 , 1 , 2 , 2 , 3 , 3 ] y_pred = [1 , 1 , 2 , 2 , 3 , 2 ] print (f"Accuacy Score : {accuracy_score(y_true, y_pred)} " )
召回率 recall_score() 計算正標籤正確比例
1 2 3 from sklearn.metrics import recall_score ... recall_score(y_true, y_pred, sample_weight=None )
y_true : 真實目標值陣列
y_pred : 模型預測值
sample_weight : option,可提供各個權重
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 from sklearn.metrics import recall_scorey_true = [1 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 1 ] y_pred = [1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 1 ] print (f"Recall Score : {recall_score(y_true, y_pred)} " )
F1 分數 f1_score() F1 分數是精確率(Precision)和召回率(Recall)的調和平均數,對於不平衡的數據集,F1分數是一個較好的指標
1 2 3 from sklearn.metrics import f1_score ... f1_score(t_true, t_pred, sample_weight=None )
公式如下 :
計算步驟 :
真正類(True Positives,TP):正確預測為正類的數量。
偽正類(False Positives,FP):錯誤預測為正類的數量。
偽負類(False Negatives,FN):錯誤預測為負類的數量。
真負類(True Negatives,TN):正確預測為負類的數量。
精確率(Precision) = TP / (TP + FP)Recall)/(Precision+Recall) = 2 * (1 0.75)/(1+0.75) = 0.8571428571
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 from sklearn.metrics import f1_scoret_true = [1 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 1 ] t_pred = [1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 1 ] print (f"F1 Score : {f1_score(t_true, t_pred)} " )
分類報告 classification_report() 分類報告提供多個類別的性能指標
精確度(Precision):
召回率(Recall):
F1分數(F1 Score)
準確度(Accuracy)
算術平均(Macro average):對每個類別進行算術平均
加權平均(Weighted average):對每個類別進行加權平均
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 from sklearn.metrics import classification_reporty_true = [1 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 1 ] y_pred = [1 , 0 , 1 , 1 , 1 , 0 , 1 ] report = classification_report(y_true, y_pred) print ("分類報告 :" )print (report)
混淆矩陣 confusion_maxtrix() 列(row)表實際類別,行(column)表預測類別
1 2 from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrixconfusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred, sample_weight=None )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrixy_true = [1 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 1 ] y_pred = [1 , 0 , 1 , 1 , 1 , 0 , 1 ] cm = confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred) print ("混淆矩陣 :" )print (cm)
ROC_AUC 分數 roc_auc_score() 用於衡量二元分類器性能的函數
1 2 3 from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score ... roc_auc_score(y_true, y_scores)
y_true : 真實標籤,通常以0和1的形式出現,某些情況下可能是-1和1
y_pred : 分類器預測為正類(1)的機率
返回0和1間的分數,越接近1,模型性能越好.越接近0,模型性能越差.若為0.5,相當於隨機猜測.
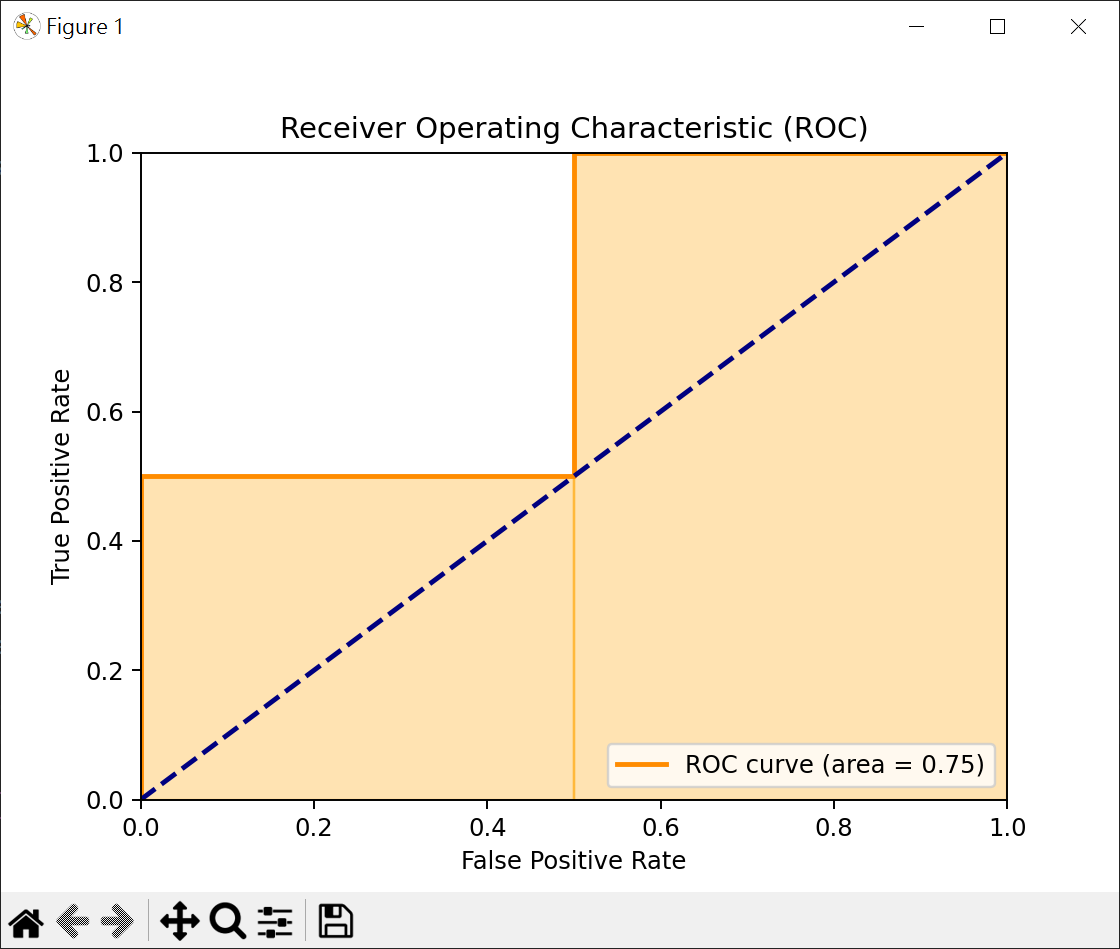
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 import matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score, roc_curvey_true = [0 , 0 , 1 , 1 ] y_scores = [0.1 , 0.4 , 0.35 , 0.8 ] auc_score = roc_auc_score(y_true, y_scores) print (f"ROC AUC 分數 : {auc_score} " )fpr, tpr, thresholds = roc_curve(y_true, y_scores) print (f"fpr={fpr} " )print (f"tpr={tpr} " )print (f"thresholds={thresholds} " )plt.figure() plt.plot(fpr, tpr, color='darkorange' , lw=2 , label=f'ROC curve (area = {auc_score:.2 f} )' ) plt.plot([0 , 1 ], [0 , 1 ], color='navy' , lw=2 , linestyle='--' ) for i in range (1 , len (fpr)): plt.fill_betweenx([0 , tpr[i]], fpr[i-1 ], fpr[i], color='orange' , alpha=0.3 ) plt.xlim([0.0 , 1.0 ]) plt.ylim([0.0 , 1.0 ]) plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate' ) plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate' ) plt.title('Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC)' ) plt.legend(loc='lower right' ) plt.show()
面積計算 = 0.5 * 0.5 + 0.5 * 1 = 0.75
機器學習必須學會的非數值資料轉換 One-hot 編碼 One-hot編碼是一種將類別行變數轉為數執行變數的方法.
df : 要進行編碼的 DataFrame
columns : 要進行編碼的欄位名稱,None 表對所有欄位
prefix : 對虛擬變數添加的前綴(default None)
prefix_sep : 連接原始欄位名稱和類別名稱的分隔符
drop_first : 是否刪除第一個類別的虛擬變數
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 import pandas as pddata = {"color" : ["red" , "blue" , "green" , "blue" ] } df = pd.DataFrame(data) print (df)encoded_df = pd.get_dummies(df, columns=['color' ]) print (encoded_df)
特徵名稱由中文改為英文 pd.rename 用於重命名 DataFrame 或 Series 中的標籤(column或index)
mapper : 字典或函數,用於指定新舊標籤之間的映射關係
index : 與 mapper 類似,用於指定索引重命名的映射
columns : 與 mapper 類似,用於指定列重命名的映射
axis : 指定沿哪個軸進行重命名,0 或 ‘index’ 表示重命名索引,1 或 ‘columns’ 表示重命名列。
inplace : 默認為 False。如果設置為 True,則會在原 DataFrame 上進行修改,而不返回新對象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 import pandas as pddf = pd.read_csv("個人資料.csv" ) pd.set_option('display.unicode.ambiguous_as_wide' , True ) pd.set_option('display.unicode.east_asian_width' , True ) print (df)print (df.columns)columns = { "編號" :"ID" , "學歷" :"Education" } df.rename(columns=columns, inplace=True ) print (df.head())
資料對應 map() 方法 pd.map() 可轉換資料為數值資料,字典key是原始資料,直是替換結果
1 2 edu = {'高中' :1 , '大學' :2 , '碩士' :3 , '博士' :4 , 'high_school' :99 } df['Education' ] = df['Education' ].map (edu)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 import pandas as pdiris = pd.Series([0 , 1 , 2 ]) print (f"執行 map() 前\n{iris} " )iris = iris.map ({0 :'setosa' , 1 :'versicolor' , 2 :'virginica' }) print (f"執行 map() 後\n{iris} " )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 import pandas as pddf = pd.read_csv("個人資料.csv" ) pd.set_option('display.unicode.ambiguous_as_wide' , True ) pd.set_option('display.unicode.east_asian_width' , True ) columns = { "編號" :"ID" , "學歷" :"Education" } df.rename(columns=columns, inplace=True ) edu = {'高中' :1 , '大學' :2 , '碩士' :3 , '博士' :4 , 'high_school' :99 } df['Education' ] = df['Education' ].map (edu) print (df.head())
標籤轉換 LabelEncoder() LabelEncoder() 可將標籤轉換為0 ~ n_classs-1值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoderfruits = ['apple' , 'apple' , 'chery' , 'apple' , 'chery' , 'orange' ] label = LabelEncoder() fruits_encoded = label.fit_transform(fruits) print (fruits_encoded)print (label.inverse_transform(fruits_encoded))
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoderfrom sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressorimport numpy as npfeatures =[['晴' ,'熱' ,'弱' ], ['晴' ,'熱' ,'強' ], ['陰' ,'熱' ,'弱' ], ['雨' ,'涼' ,'弱' ], ['雨' ,'冷' ,'弱' ], ['雨' ,'冷' ,'強' ], ['陰' ,'冷' ,'強' ]] features_encoded = [] for i in range (len (features[0 ])): le = LabelEncoder() feature_encoded = le.fit_transform([row[i] for row in features]) features_encoded.append(feature_encoded) features_encoded = np.array(features_encoded).T print (f"特徵標籤編碼\n{features_encoded} " )
機器學習演算法
監督學習法
線性迴歸
邏輯迴歸
KNN 演算法
支持向量機(SVM)
決策樹
隨機森林
無監督學習法
分群(或稱聚類)分析(如:K-means)
降維(如:主成份分析(PCA))
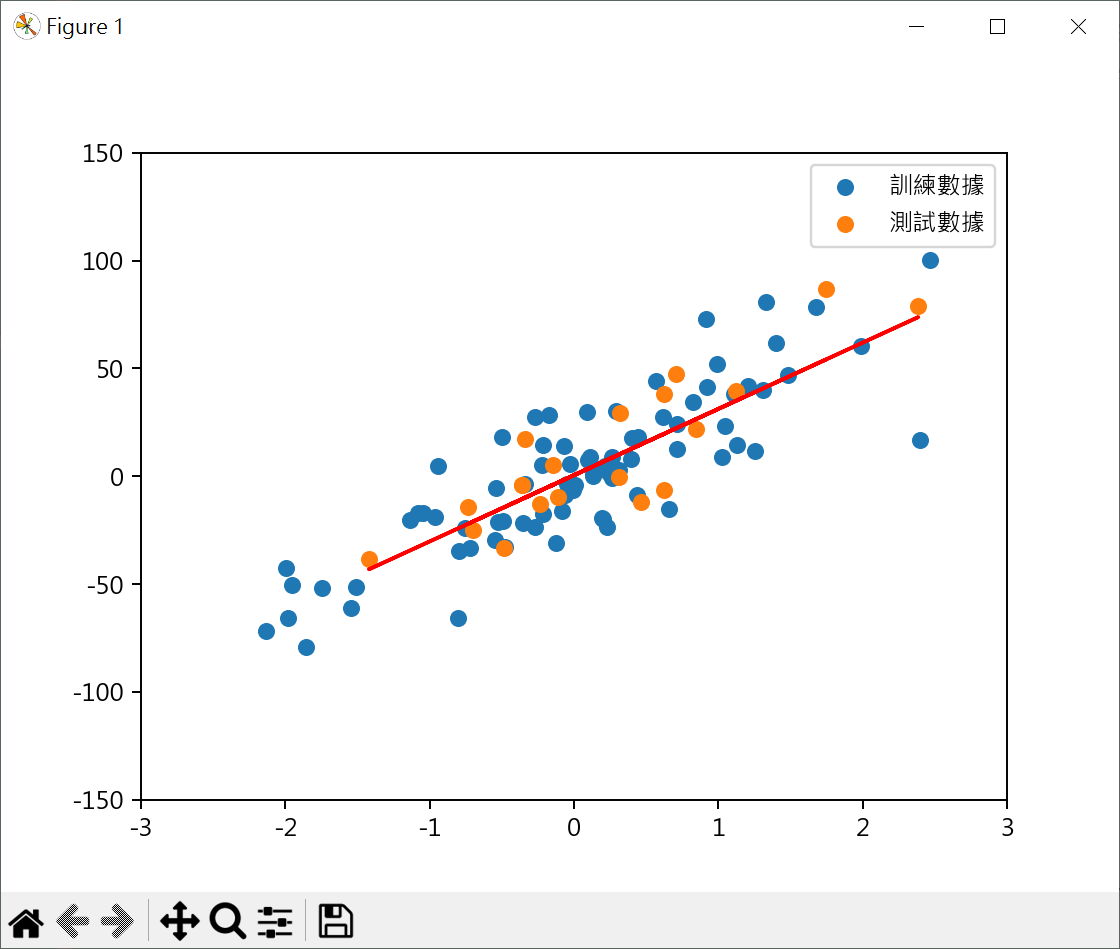
使用隨機數據學習性迴歸 使用隨機數據測試迴歸模型 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 from sklearn.datasets import make_regressionfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegressionfrom sklearn.metrics import r2_scoreimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltplt.rcParams["font.family" ] = ["Microsoft JhengHei" ] plt.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus" ] = False X, y = make_regression(n_features=1 , noise=20 , random_state=10 ) X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = \ train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2 , random_state=10 ) model = LinearRegression() model.fit(X=X_train, y=y_train) plt.scatter(X_train, y_train, label="訓練數據" ) plt.scatter(X_test, y_test, label="測試數據" ) y_pred = model.predict(X_test) plt.plot(X_test, y_pred, color='red' ) print (f"R2_Score:{r2_score(y_test, y_pred):.2 f} " )plt.legend() plt.axis([-3 , 3 , -150 , 150 ]) plt.show()
score() 和 r2_score() 的差異 scikit-learn 中 score() 和 r2_score() 都可以計算R平方判定係數,但場景有一些差異
如果你想快速地在個模型上計算R平方判定係數,score(X, y)較方便,如你需要更多的靈活性,如比對不同模型的預測效果,或你已有預測結果,r2_score(y_true, y_pred)可能更適合
其他 儲存公式 # 邏輯迴歸模型語法基礎
數據 創建聚類算法的測試數據集 # 繪製散點圖
生成合成線性回歸數據集 # 線性回歸數據集-繪製散點圖
邏輯迴歸 基本計算 # 邏輯迴歸模型語法基礎
特徵縮放 - 對邏輯迴歸很重要,因各特徵數值大小有差異 # 用最相關2個特徵,設計邏輯迴歸模型
決策樹 基本例子 # 天氣數據實例
繪製決策樹 # 繪製決策樹