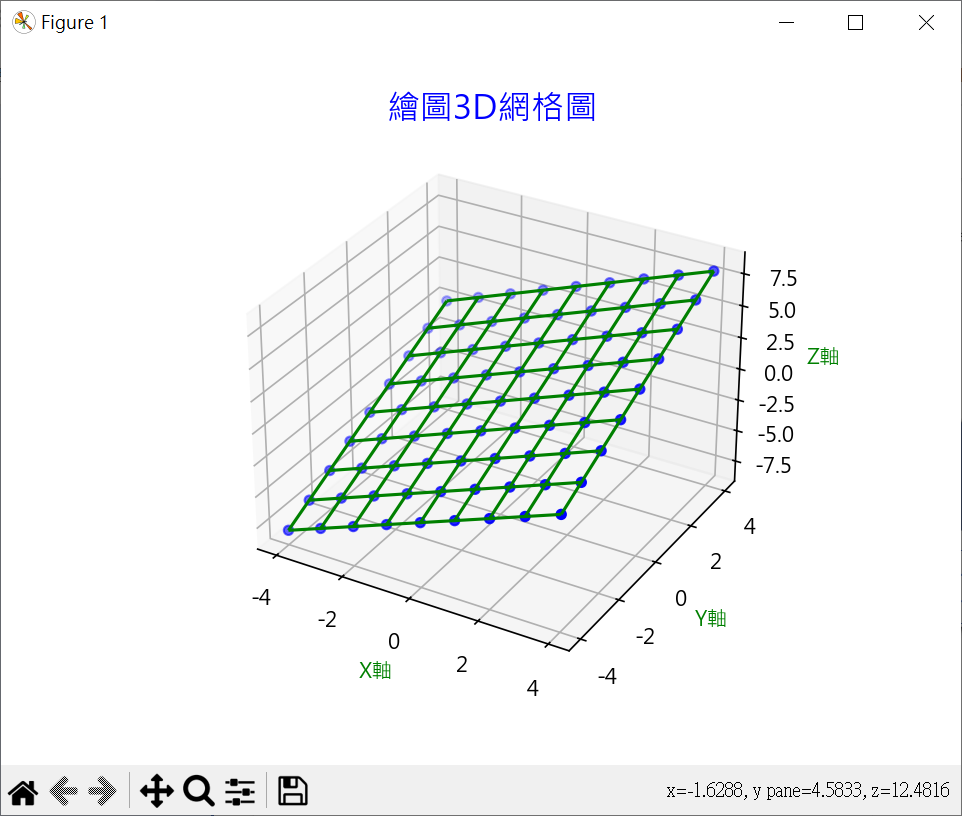
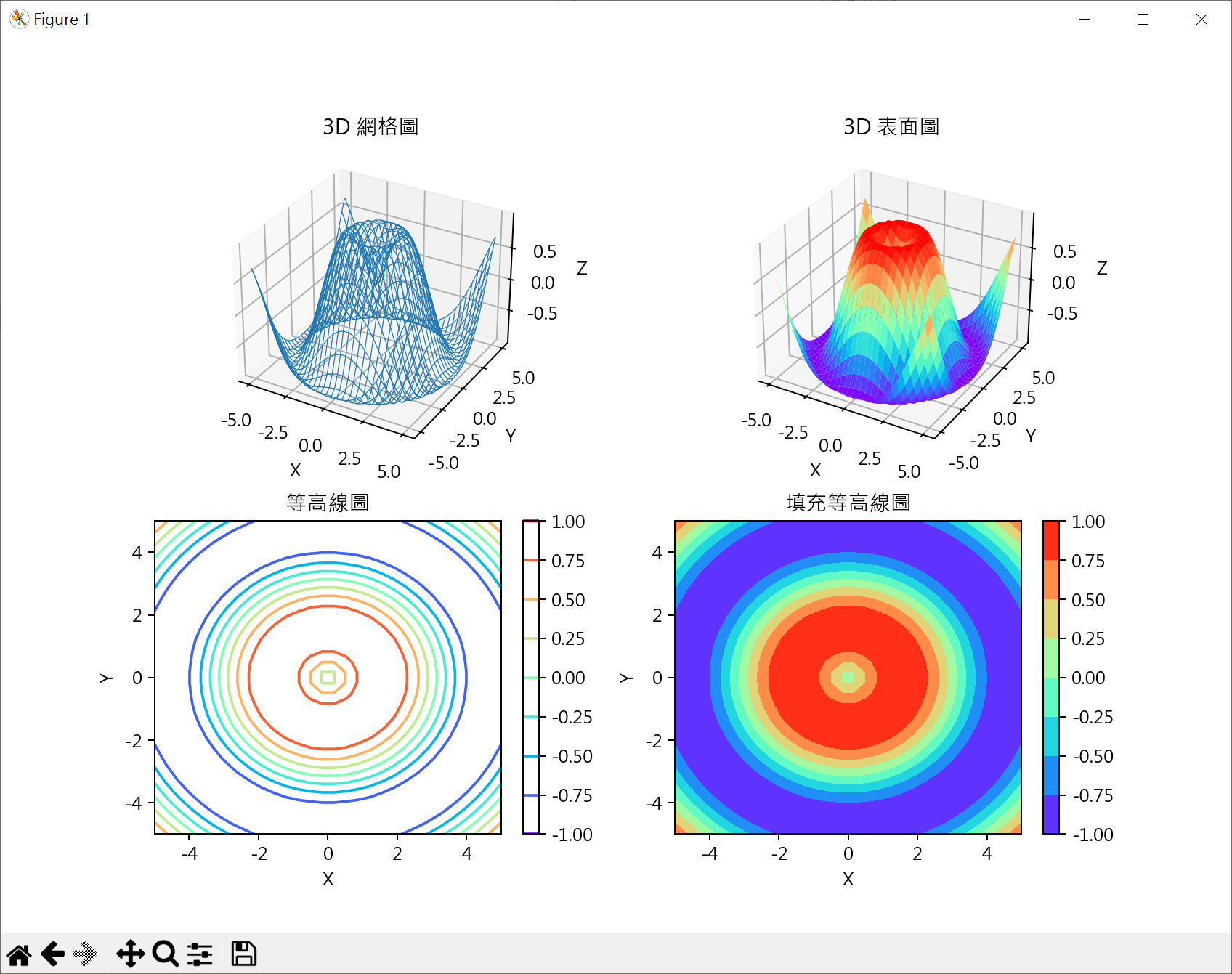
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = ["Microsoft JhengHei"]
plt.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus"] = False
x = np.linspace(-5, 5, 30)
y = np.linspace(-5, 5, 30)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
Z = np.sin(np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2))
fig = plt.figure(figsize= (10, 6))
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(221, projection='3d')
ax1.plot_wireframe(X, Y, Z, linewidth=0.5, cmap="rainbow")
ax1.set_title('3D 網格圖')
ax1.set_xlabel('X')
ax1.set_ylabel('Y')
ax1.set_zlabel('Z')
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(222, projection='3d')
ax2.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, cmap="rainbow")
ax2.set_title('3D 表面圖')
ax2.set_xlabel('X')
ax2.set_ylabel('Y')
ax2.set_zlabel('Z')
ax3 = fig.add_subplot(223)
countour = ax3.contour(X, Y, Z, cmap="rainbow")
ax3.set_title('等高線圖')
ax3.set_xlabel('X')
ax3.set_ylabel('Y')
fig.colorbar(countour)
ax4 = fig.add_subplot(224)
countourf = ax4.contourf(X, Y, Z, cmap="rainbow")
ax4.set_title('填充等高線圖')
ax4.set_xlabel('X')
ax4.set_ylabel('Y')
fig.colorbar(countourf)
plt.show()
|