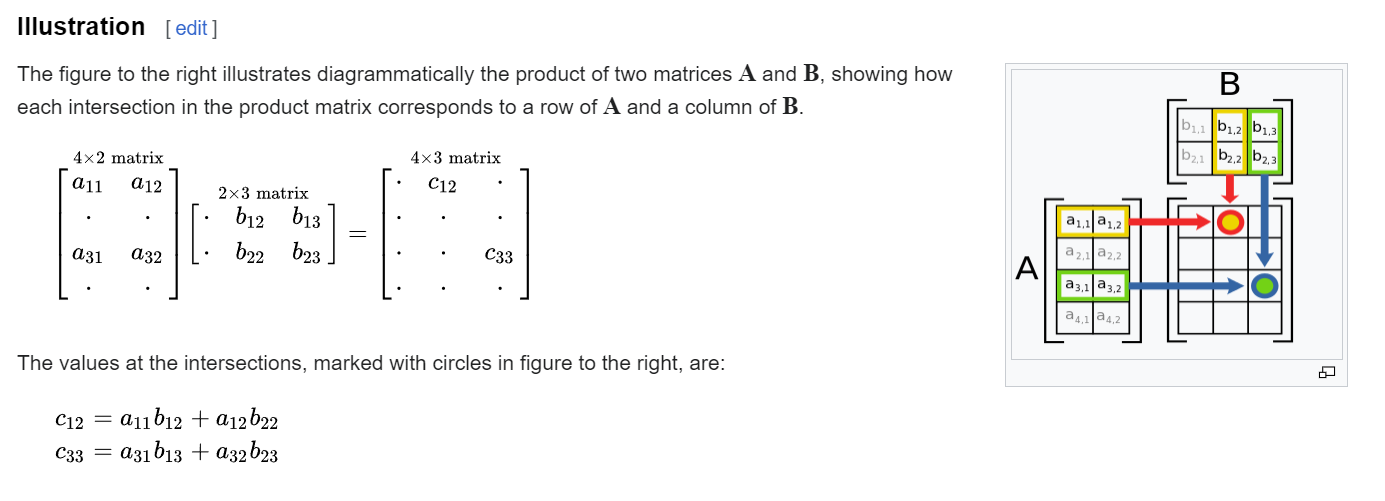
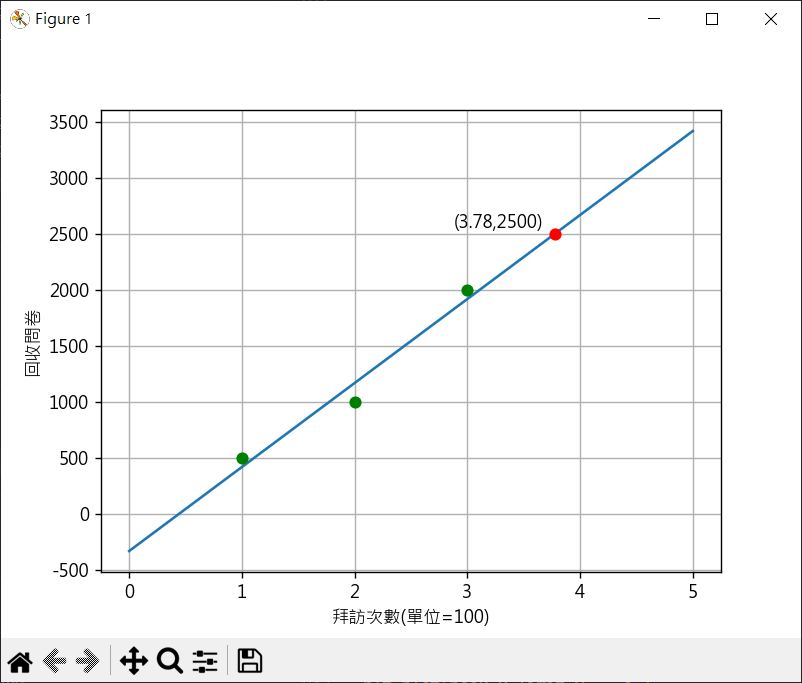
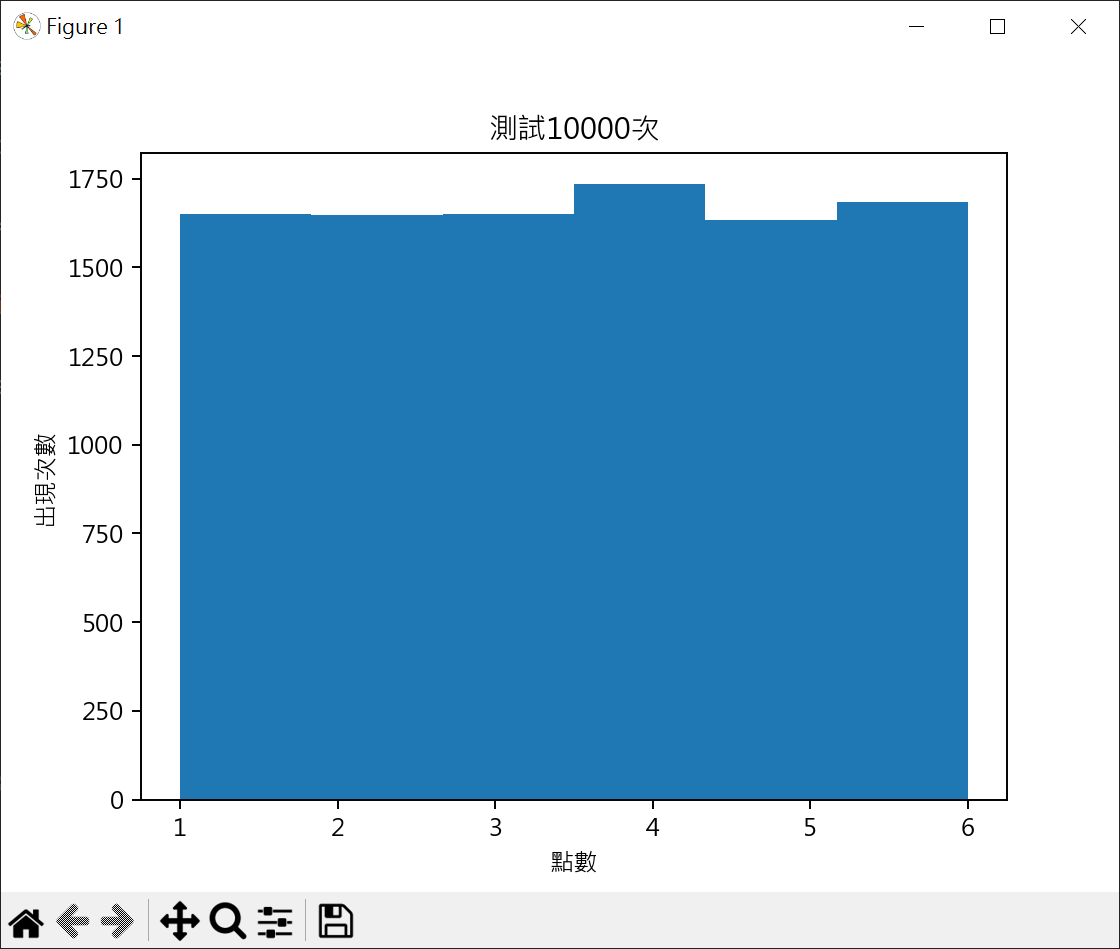
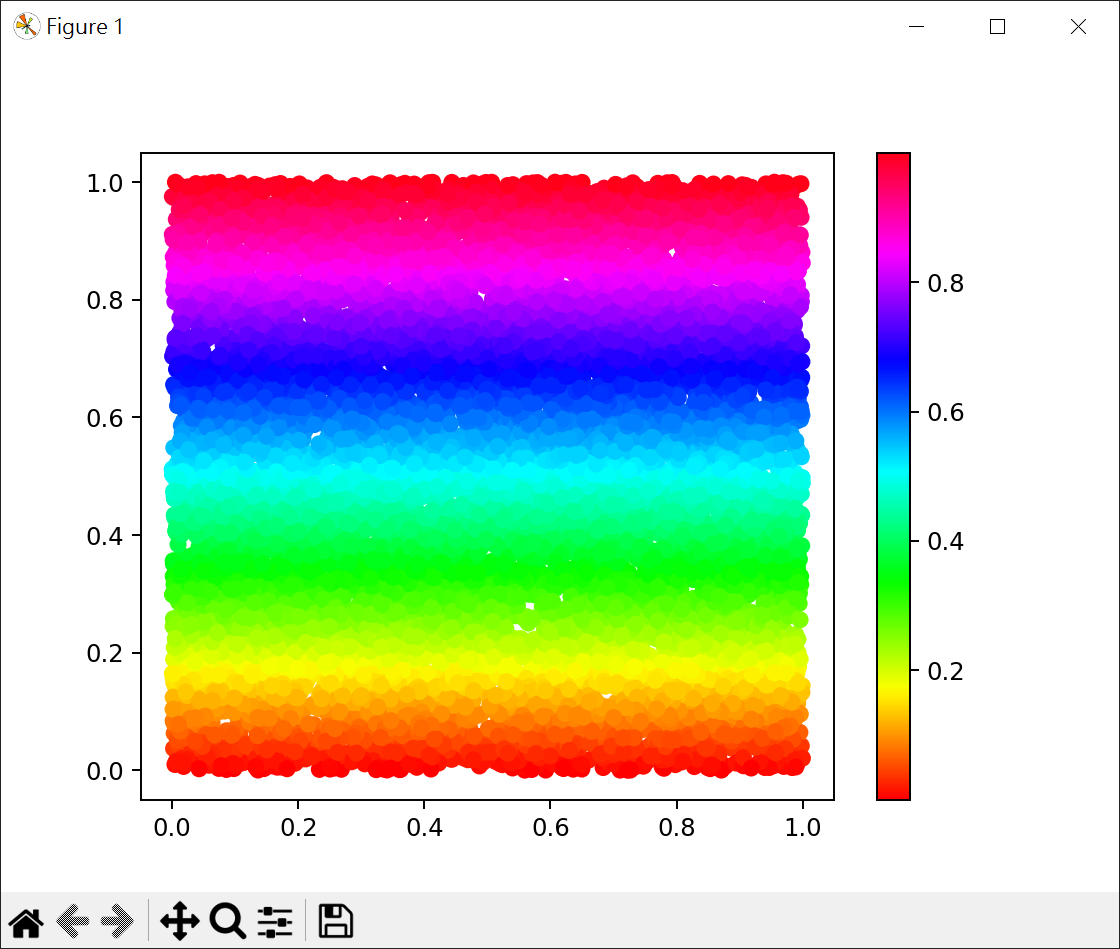
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
| import numpy as np
A = np.matrix([[1,2],
[3, 4]])
B = np.matrix([[5,6],
[7,8]])
print(f"A + B = {A + B}")
print(f"A * B = {A * B}")
A = np.matrix([[2, 3],
[5, 7]])
B = np.linalg.inv(A)
A = np.array([
[[1,2],
[3,4]],
[[5,6],
[7,8]],
[[9,10],
[11,12]],
])
print(f"shape = {np.shape(A)}")
A = np.array([[0, 2, 4, 6],
[1, 3, 5, 7]])
B = A.T
print(f"轉置矩陣1 = {B}")
C = np.transpose(A)
print(f"轉置矩陣2 = {C}")
height = np.array([1.6, 1.63, 1.71, 1.73, 1.83]).reshape(-1,1)
RSS = np.sum((weight - np.ravel(model.predict(height))) ** 2)
print(X[:5])
print(f"X[:,0] 前 5 個樣本")
xx = X[:,0]
print(xx[:5])
print(f"X[:,1] 前 5 個樣本")
xx = X[:,1]
print(xx[:5])
|