CS50AI
Search
Term
1 | agent |
shell
1 | # install |
project submit
put to github
1 | # degress git |

submit
1 | # switch to new brance |

modify then submit
1 | # tictactoe |
update my repository
1 | # push to my repository |
knowledge
Term
1 | # Entailment (語義蘊涵也叫做邏輯蘊涵⊨) |
1 | # → |
example code
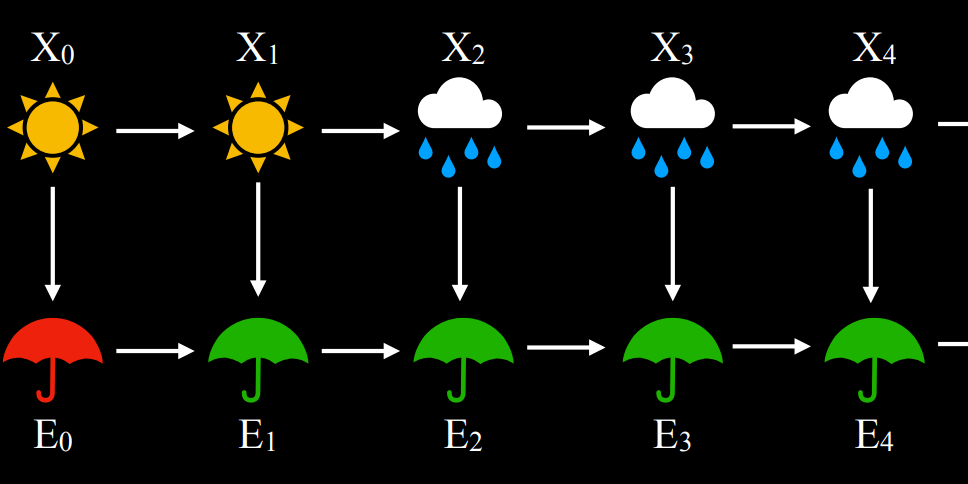
rain?
1 | from logic import * |
clue
1 | import termcolor |
Inference Rules(推理規則)
1 | # modus ponens 正向思維律 |
Theorem Proving(定理證明)
1 | • initial state: starting knowledge base |
Resolution(歸結原理)
1 | (P ∨ Q) (¬P) --> Q |
Conversion to CNF
1 | # Clauses allow us to convert any logical statement into a Conjunctive Normal Form (CNF), which is a conjunction of clauses, for example: (A ∨ B ∨ C) ∧ (D ∨ ¬E) ∧ (F ∨ G). |
Inference by Resolution
1 | (P ∨ Q) (¬P ∨ R) --> (Q ∨ R) |
First-Order Logic
1 | First-Order Logic |
Uncertainty
Conditional Probability 條件機率
1 | P(a|b) = P(a∧b)/P(b) |
Bayes’ Rule(貝葉斯法則)
1 | P(a|b) = P(a∧b)/P(b) |
Joint Probability(聯合機率)
1 | C = cloud C = ¬cloud |
Probability Rules(機率規則)
1 | Negation: P(¬a) = 1 - P(a). |
Bayesian Networks(貝葉斯網絡)
1 | - They are directed graphs. |
Inference
1 | - Query X: the variable for which we want to compute the probability distribution. |
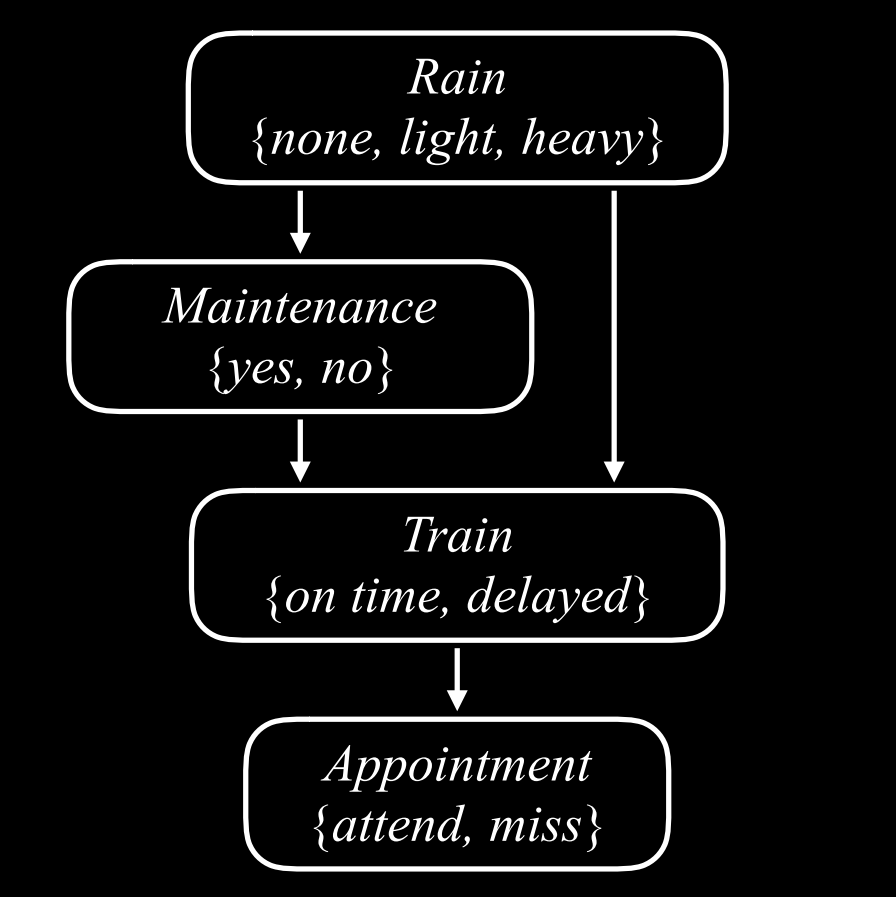
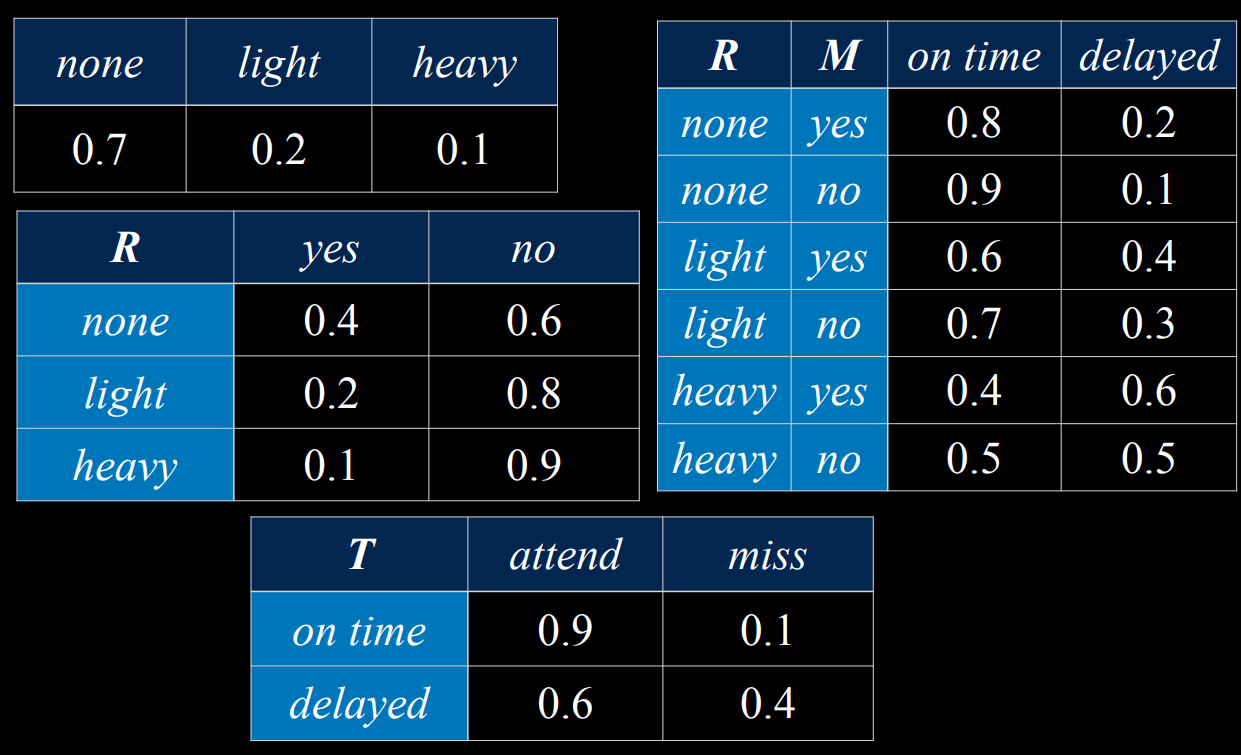
Bayesian Networks
inastall pomegranate (need correct version)
1 | pip3 install pomegranate==v0.14.9 |
Inference by Enumeration列舉 #1 - give condition –> attend/miss probability
model.py
1 | from pomegranate import * |
likelihood.py
1 | from model import model |
result
1 | python .\likelihood.py |
Inference by Enumeration #2 - train delayed –> predict attend/miss probability
inference.py
1 | from model import model |
Sampling取樣 - approximate inference 近似推理
sample.py
1 | import pomegranate |
result
1 | python .\sample.py |
Likelihood Weighting 可能性加權
1 | - Start by fixing the values for evidence variables. |
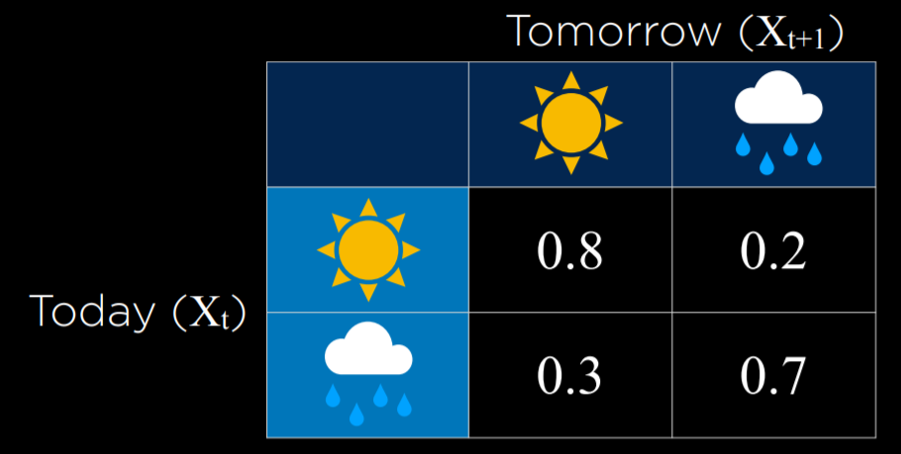
Markov Model
1 | - Markov Assumption 馬卡夫假設 |

model.py
1 | from pomegranate import * |
result
1 | python .\model.py |
Markov Models #2
1 | - Hidden Markov Models |

model.py
1 | from pomegranate import * |
sequence.py
1 | from model import model |
result
1 | python .\sequence.py |
Optimization
Term
1 | Local search |
Learning
Term
1 | Learning |
banknotes0.py
1 | import csv |
banknotes1.py
1 | import csv |
Neural Networks
Term
1 | artificial neural network(ANN)人工神經網路 |
content
Neural Network Structure
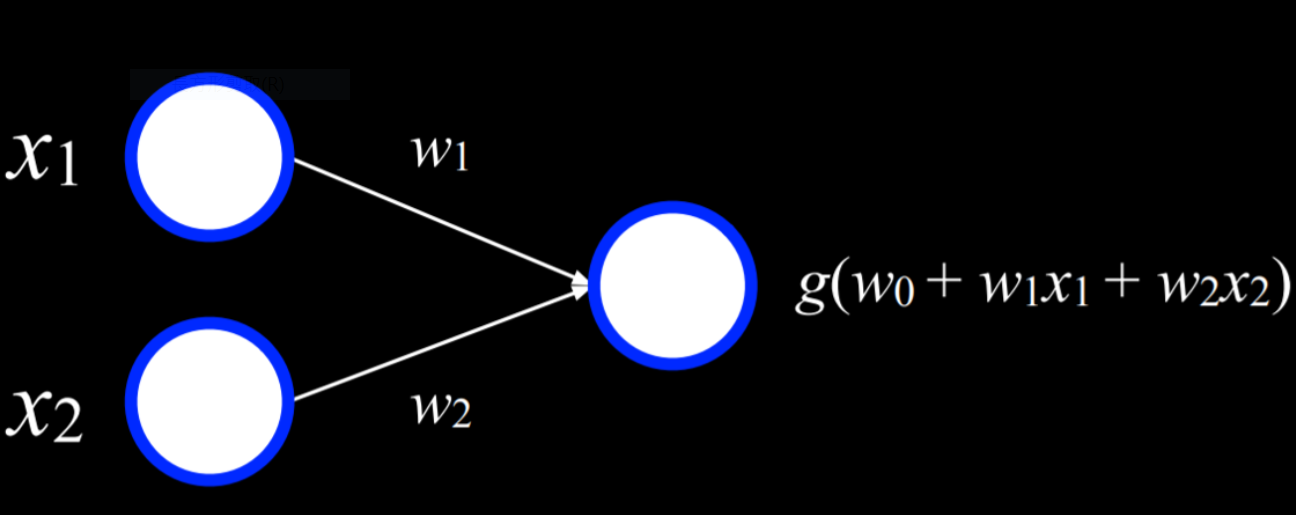
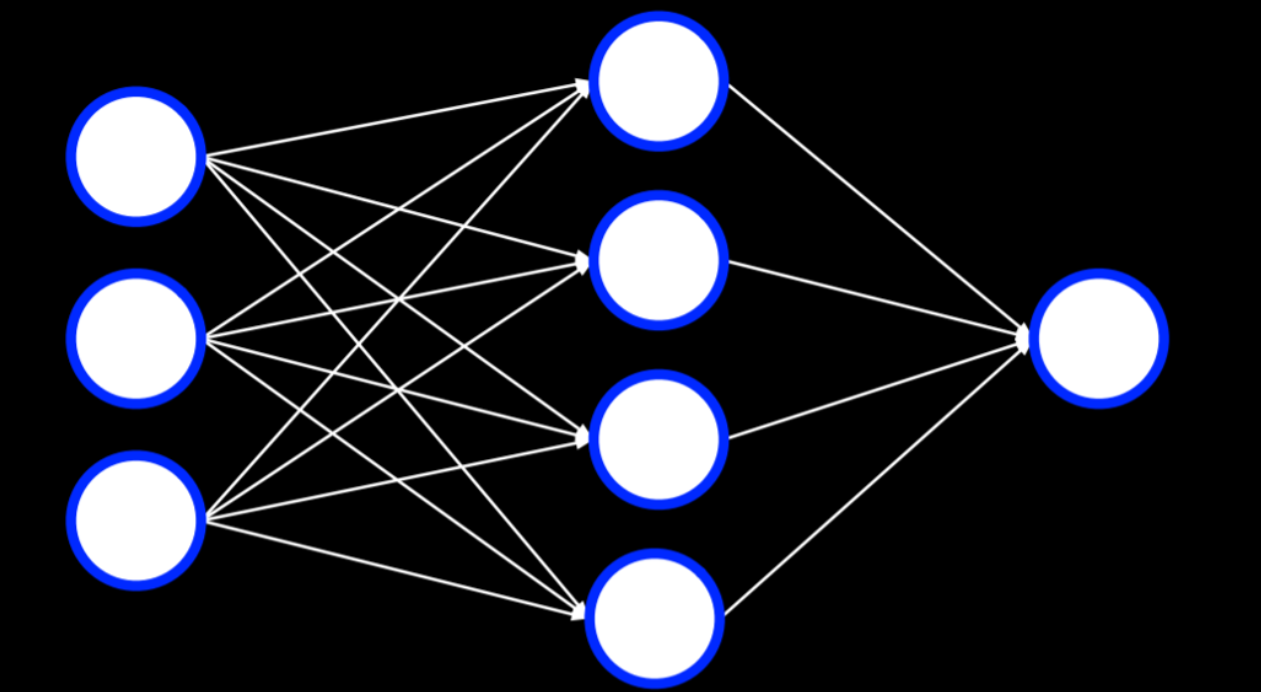
Multilayer Neural Networks
Overfitting

Image Convolution
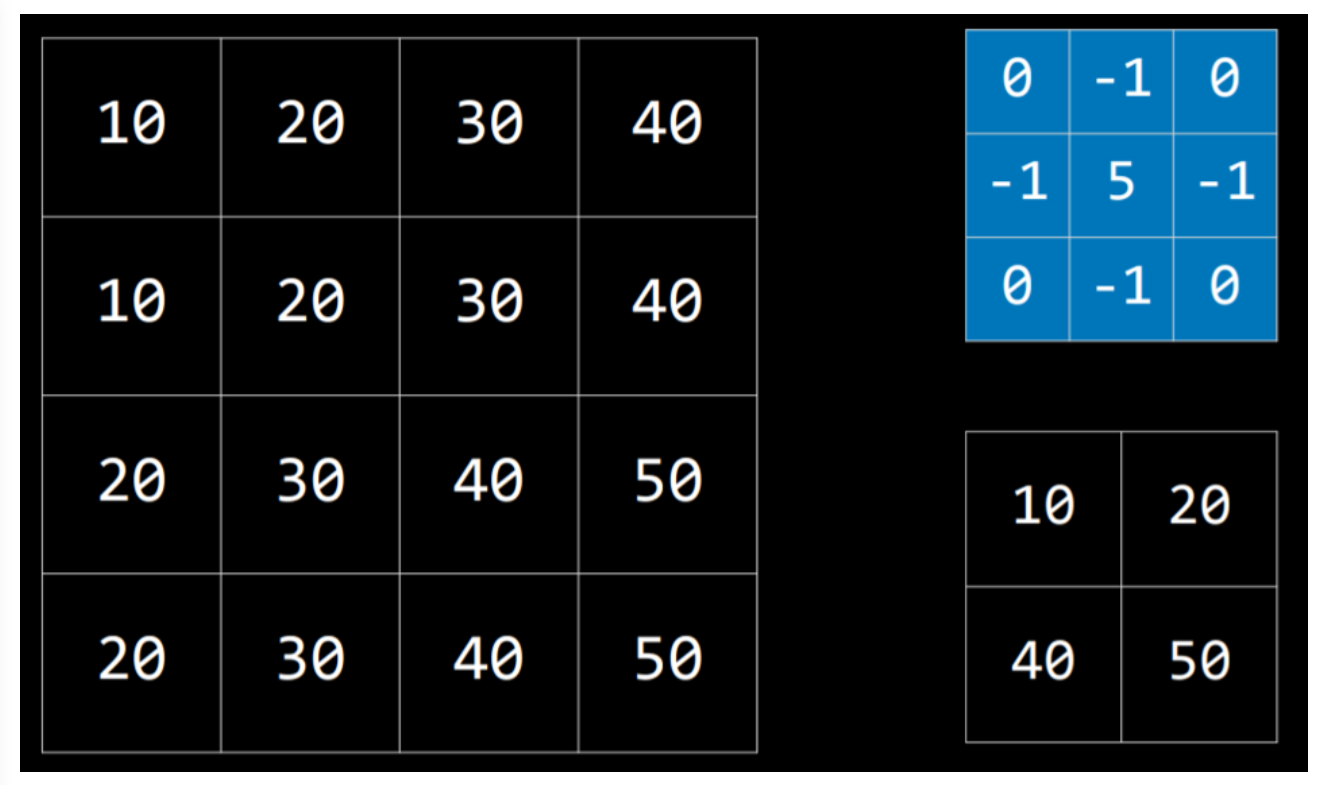
max-pooling

Convolutional Neural Networks

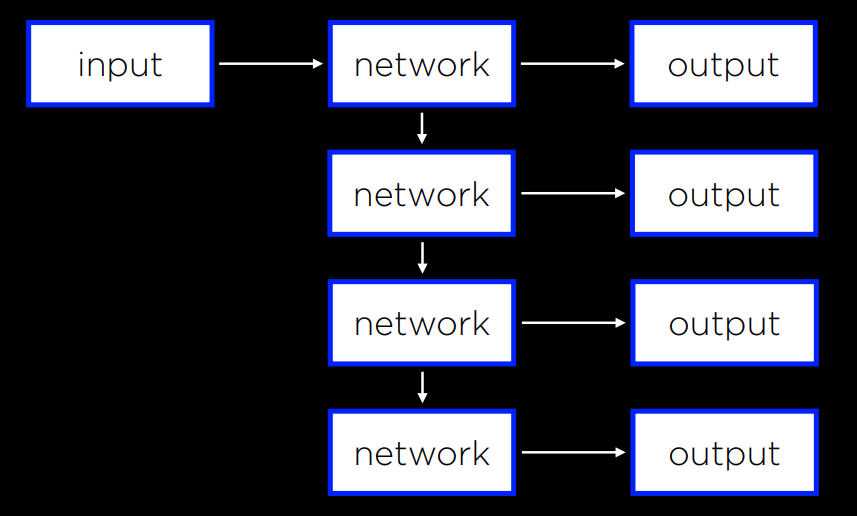
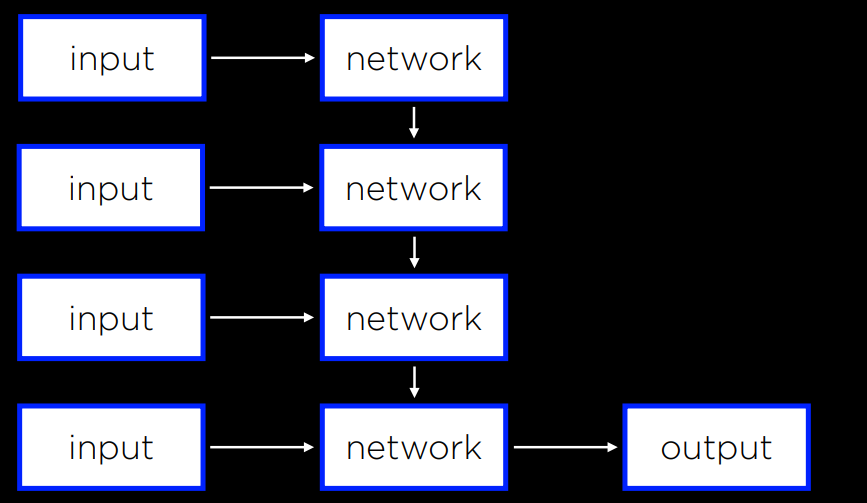
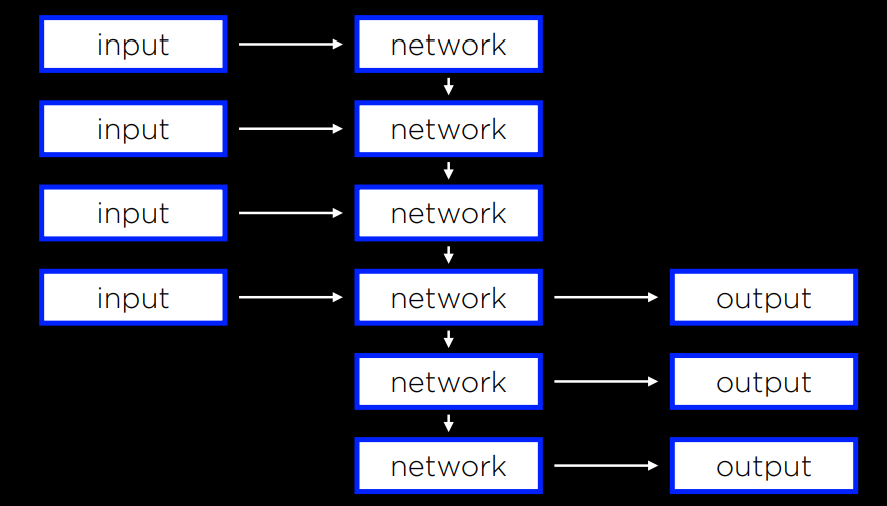
recurrent neural network
CaptionBot
Youtub
google 翻譯
code
banknotes.py
1 | import csv |
filter.py
1 | import math |
handwriting.py
1 | import sys |
Python
setup
1 | # check which python |
package
list
1 | # SciPy Python : 演算法庫和數學工具包 |
csv
1 | import csv |
syntax
anonymous functions
1 | testGreedy(foods, maxUnits, |
1 | >>> f1 = lambda x: x |
class print function : string
1 | class Food(object): |
@classmethod
1 | class MyClass: |
dict - key by tuple
1 | self.q = dict() |
function
sorted
1 | def buildMenu(names, values, calories): |
zip
1 | # example |
copy
1 | # copy to new variable |
items
1 | # self.q.items() returns a view of the dictionary's key-value pairs, |
tuple - list –> tuple
1 | q = self.q[tuple(state), move] |